Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 4β-N-Acetylamino Substituted Podophyllotoxin Derivatives as Novel Anticancer Agents
- PMID: 31106192
- PMCID: PMC6491884
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00253
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 4β-N-Acetylamino Substituted Podophyllotoxin Derivatives as Novel Anticancer Agents
Abstract
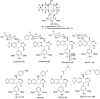
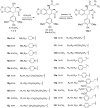
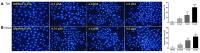
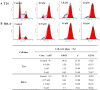
A series of novel podophyllotoxin derivatives obtained by 4β-N-acetylamino substitution at C-4 position was designed, synthesized, and evaluated for in vitro cytotoxicity against four human cancer cell lines (EC-9706, HeLA, T-24 and H460) and a normal human epidermal cell line (HaCaT). The cytotoxicity test indicated that most of the derivatives displayed potent anticancer activities. In particular, compound 12h showed high activity with IC50 values ranging from 1.2 to 22.8 μM, with much better cytotoxic activity than the control drug etoposide (IC50: 8.4 to 78.2 μM). Compound 12j exhibited a promising cytotoxicity and selectivity profile against T24 and HaCaT cell lines with IC50 values of 2.7 and 49.1 μM, respectively. Compound 12g displayed potent cytotoxicity against HeLA and T24 cells with low activity against HaCaT cells. According to the results of fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis, 12g induced cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase accompanied by apoptosis in T24 and HeLA cells. Furthermore, the docking studies showed possible interactions between human DNA topoisomerase IIα and 12g. These results suggest that 12g merits further optimization and development as a new podophyllotoxin-derived lead compound.
Keywords: C-4 substitutions; anticancer agent; biological evaluation; podophyllotoxin derivatives; structure–activity relationships (SAR).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synthesis and anticancer activity of dimeric podophyllotoxin derivatives.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Oct 9;12:3393-3406. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S167382. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 30349193 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Biological evaluation of novel 4β-[(5-substituted)-1,2,3,4-tetrazolyl] podophyllotoxins as anticancer compounds.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Jul 15;25(14):2860-3. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.04.053. Epub 2015 May 5. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015. PMID: 26022842
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 4β-(1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-amino)-podophyllotoxin derivatives.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Jul 15;22(14):4778-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.05.059. Epub 2012 May 23. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012. PMID: 22687745
-
Antitumor properties of podophyllotoxin and related compounds.Curr Pharm Des. 2000 Dec;6(18):1811-39. doi: 10.2174/1381612003398582. Curr Pharm Des. 2000. PMID: 11102564 Review.
-
Insight Into the Molecular Mechanism of Podophyllotoxin Derivatives as Anticancer Drugs.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 10;9:709075. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.709075. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34447752 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular Distribution and Ultrastructural Changes in HaCaT Cells, Induced by Podophyllotoxin and Its Novel Fluorescent Derivative, Supported by the Molecular Docking Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 29;25(11):5948. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115948. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892135 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Podophyllotoxin Derivatives on Noncancerous Diseases: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 23;26(3):958. doi: 10.3390/ijms26030958. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940726 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic and Naturally Occurring Heterocyclic Anticancer Compounds with Multiple Biological Targets.Molecules. 2021 Nov 25;26(23):7134. doi: 10.3390/molecules26237134. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34885716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Podophyllotoxin: Recent Advances in the Development of Hybridization Strategies to Enhance Its Antitumoral Profile.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Dec 4;15(12):2728. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15122728. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38140069 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen Y. F., Lin Y. C., Huang P. K., Chan H. C., Kuo S. C., Lee K. H., et al. . (2013). Design and synthesis of 6,7-methylenedioxy-4-substituted phenylquinolin-2(1H)-one derivatives as novel anticancer agents that induce apoptosis with cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 21, 5064–5075. 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.06.046 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Damayanthi Y., Lown J. W. (1998). Podophyllotoxins: current status and recent developments. Curr. Med. Chem. 5, 205–252. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

