De Novo Interstitial Deletion of 9q in a Pediatric Patient With Global Developmental Delay
- PMID: 31106228
- PMCID: PMC6506918
- DOI: 10.1177/2329048X19844920
De Novo Interstitial Deletion of 9q in a Pediatric Patient With Global Developmental Delay
Abstract
Cytogenomic microarray (CMA) methodologies, including array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) and single-nucleotide polymorphism-detecting arrays (SNP-array), are recommended as the first-tier test for the evaluation of imbalances associated with intellectual disability, autism, and multiple congenital anomalies. The authors report on a child with global developmental delay (GDD) and a de novo interstitial 7.0 Mb deletion of 9q21.33q22.31 detected by aCGH. The patient that the authors report here is noteworthy in that she presented with GDD and her interstitial deletion is not inclusive of the 9q22.32 locus that includes the PTCH1 gene, which is implicated in Gorlin syndrome, or basal cell nevus syndrome (BCNS), has not been previously reported among patients with a similar or smaller size of the deletion in this locus suggesting that the genomic contents in the identified deletion on 9q21.33q22.31 is critical for the phenotype.
Keywords: behavior; children; developmental delay; developmental disability; genetics; infant; intellectual disability; mutation; neonate; pediatric.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
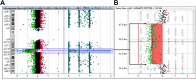


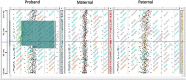
Similar articles
-
Rare Case of a Heterozygous Microdeletion 9q21.11-q21.2: Clinical and Genetic Characteristics.Balkan J Med Genet. 2018 Dec 31;21(2):59-62. doi: 10.2478/bjmg-2018-0021. eCollection 2018 Dec. Balkan J Med Genet. 2018. PMID: 30984527 Free PMC article.
-
Unexpected phenotype in a frameshift mutation of PTCH1.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Jan;8(1):e987. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.987. Epub 2019 Oct 2. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. PMID: 31578813 Free PMC article.
-
Microdeletion 9q22.3 syndrome includes metopic craniosynostosis, hydrocephalus, macrosomia, and developmental delay.Am J Med Genet A. 2012 Feb;158A(2):391-9. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.34216. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Am J Med Genet A. 2012. PMID: 22190277
-
Medical genetics diagnostic evaluation of the child with global developmental delay or intellectual disability.Curr Opin Neurol. 2008 Apr;21(2):117-22. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0b013e3282f82c2d. Curr Opin Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18317267 Review.
-
Gorlin syndrome patient with large deletion in 9q22.32-q22.33 detected by quantitative multiplex fluorescent PCR.Dermatology. 2009;219(2):111-8. doi: 10.1159/000219247. Epub 2009 May 14. Dermatology. 2009. PMID: 19439922 Review.
References
-
- Shevell M, Ashwal S, Donley D, et al. Practice parameter: evaluation of the child with global developmental delay: report of the quality standards subcommittee of the american academy of neurology and the practice committee of the child neurology society. Neurology. 2003;60(3):367–380. - PubMed
-
- (CNS). AAoNAaCNS. Evaluation of the Child with Global Developmental Delay Guideline Summary for Clinicians 2013. Accessed April, 2018.
-
- Shevell MI, Majnemer A, Rosenbaum P, Abrahamowicz M. Etiologic yield of subspecialists’ evaluation of young children with global developmental delay. J Pediatr. 2000;136(5):593–598. - PubMed
-
- Scott SA, Cohen N, Brandt T, Toruner G, Desnick RJ, Edelmann L. Detection of low-level mosaicism and placental mosaicism by oligonucleotide array comparative genomic hybridization. Genet Med. 2010;12(2):85–92. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

