Calcium-binding nanoparticles for vascular disease
- PMID: 31106257
- PMCID: PMC6516760
Calcium-binding nanoparticles for vascular disease
Abstract
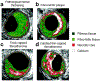
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) including atherosclerosis is the leading cause of death worldwide. As CVDs and atherosclerosis develop, plaques begin to form in the blood vessels and become calcified. Calcification within the vasculature and atherosclerotic plaques have been correlated with rupture and consequently, acute myocardial infarction. However, current imaging methods to identify vascular calcification have limitations in determining plaque composition and structure. Nanoparticles can overcome these limitations due to their versatility and ability to incorporate a wide range of targeting and contrast agents. In this review, we summarize the current understanding of calcification in atherosclerosis, their role in instigating plaque instability, and clinical methodologies to detect and analyze vascular calcification. In addition, we highlight the potential of calcium-targeting ligands and nanoparticles to create novel calcium-detecting tools.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Drug delivery; Imaging; Nanoparticle; Peptides; Vascular calcification.
Figures

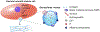
Similar articles
-
Hydroxyapatite-binding micelles for the detection of vascular calcification in atherosclerosis.J Mater Chem B. 2019 Nov 7;7(41):6449-6457. doi: 10.1039/c9tb01918a. Epub 2019 Sep 25. J Mater Chem B. 2019. PMID: 31553027 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium deposition within coronary atherosclerotic lesion: Implications for plaque stability.Atherosclerosis. 2020 Aug;306:85-95. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2020.05.017. Epub 2020 Jun 14. Atherosclerosis. 2020. PMID: 32654790 Review.
-
Targeting non-coding RNAs in unstable atherosclerotic plaques: Mechanism, regulation, possibilities, and limitations.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Aug 3;17(13):3413-3427. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.62506. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34512156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging Atherosclerotic Plaque Calcification: Translating Biology.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2016 Aug;18(8):51. doi: 10.1007/s11883-016-0601-6. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2016. PMID: 27339750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of in vivo targeting ability between cRGD and collagen-targeting peptide conjugated nano-carriers for atherosclerosis.J Control Release. 2018 Jan 10;269:337-346. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.11.033. Epub 2017 Nov 22. J Control Release. 2018. PMID: 29175140
Cited by
-
Hydroxyapatite-binding micelles for the detection of vascular calcification in atherosclerosis.J Mater Chem B. 2019 Nov 7;7(41):6449-6457. doi: 10.1039/c9tb01918a. Epub 2019 Sep 25. J Mater Chem B. 2019. PMID: 31553027 Free PMC article.
-
miR-145 micelles mitigate atherosclerosis by modulating vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype.Biomaterials. 2021 Jun;273:120810. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.120810. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Biomaterials. 2021. PMID: 33892346 Free PMC article.
-
Collagenase-Cleavable Peptide Amphiphile Micelles as a Novel Theranostic Strategy in Atherosclerosis.Adv Ther (Weinh). 2020 Mar;3(3):1900196. doi: 10.1002/adtp.201900196. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Adv Ther (Weinh). 2020. PMID: 34295964 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Study of Ultrasmall Calcium Carbonate Nanoparticles for Targeting and Imaging Atherosclerotic Plaque.ACS Nano. 2023 Jul 25;17(14):13811-13825. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c03523. Epub 2023 Jul 3. ACS Nano. 2023. PMID: 37399106 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomedicines for cardiovascular disease.Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2023 Apr;2(4):351-367. doi: 10.1038/s44161-023-00232-y. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2023. PMID: 39195953 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
