N6-methyladenosine modifications: interactions with novel RNA-binding proteins and roles in signal transduction
- PMID: 31107151
- PMCID: PMC6602412
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1620060
N6-methyladenosine modifications: interactions with novel RNA-binding proteins and roles in signal transduction
Abstract
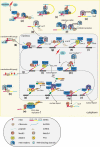
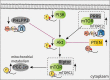
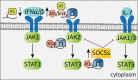
RNA epigenetics has received a great deal of attention in recent years, and the reversible N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification on messenger RNAs (mRNAs) has emerged as a widespread phenomenon. The vital roles of m6A in diverse biological processes are dependent on many RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) with 'reader' or 'nonreader' functions. Moreover, m6A effector proteins affect cellular processes, such as stem cell differentiation, tumor development and the immune response by controlling signal transduction. This review provides an overview of the interactions of m6A with various RBPs, including the 'reader' proteins (excluding the YT521-B homology (YTH) domain proteins and the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs)), and the functional 'nonreader' proteins, and this review focuses on their specific RNA-binding domains and their associations with other m6A effectors. Furthermore, we summarize key m6A-marked targets in distinct signaling pathways, leading to a better understanding of the cellular m6A machinery.
Keywords: M6a reader; RNA-binding protein; protein domain; signaling pathway.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
