ADAM17-dependent signaling is required for oncogenic human papillomavirus entry platform assembly
- PMID: 31107240
- PMCID: PMC6557631
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.44345
ADAM17-dependent signaling is required for oncogenic human papillomavirus entry platform assembly
Abstract
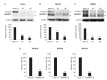
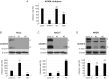
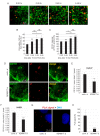
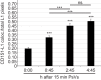
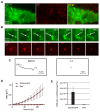
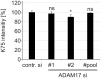
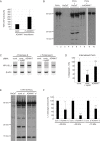
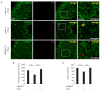
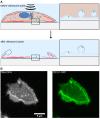
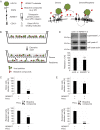
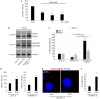
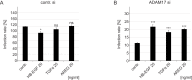
Oncogenic human papillomaviruses (HPV) are small DNA viruses that infect keratinocytes. After HPV binding to cell surface receptors, a cascade of molecular interactions mediates the infectious cellular internalization of virus particles. Aside from the virus itself, important molecular players involved in virus entry include the tetraspanin CD151 and the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). To date, it is unknown how these components are coordinated in space and time. Here, we studied plasma membrane dynamics of CD151 and EGFR and the HPV16 capsid during the early phase of infection. We find that the proteinase ADAM17 activates the extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2) pathway by the shedding of growth factors which triggers the formation of an endocytic entry platform. Infectious endocytic entry platforms carrying virus particles consist of two-fold larger CD151 domains containing the EGFR. Our finding clearly dissects initial virus binding from ADAM17-dependent assembly of a HPV/CD151/EGFR entry platform.
Keywords: ADAM17; cell biology; entry receptor complex; growth factors; human; infectious disease; microbiology; microdomains; oncogenic Papillomavirus; tetraspanin.
© 2019, Mikuličić et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SM, JF, FB, EW, DS, YH, KR, TL, LF No competing interests declared
Figures




Similar articles
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Abl2 Kinase Regulate Distinct Steps of Human Papillomavirus 16 Endocytosis.J Virol. 2020 May 18;94(11):e02143-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02143-19. Print 2020 May 18. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32188731 Free PMC article.
-
Tetraspanin CD9 affects HPV16 infection by modulating ADAM17 activity and the ERK signalling pathway.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2020 Aug;209(4):461-471. doi: 10.1007/s00430-020-00671-5. Epub 2020 May 8. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32385608 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomy of a viral entry platform differentially functionalized by integrins α3 and α6.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 24;10(1):5356. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62202-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32210347 Free PMC article.
-
The endocytic trafficking pathway of oncogenic papillomaviruses.Papillomavirus Res. 2019 Jun;7:135-137. doi: 10.1016/j.pvr.2019.03.004. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Papillomavirus Res. 2019. PMID: 30946955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The tetraspanin CD151 in papillomavirus infection.Viruses. 2014 Feb 18;6(2):893-908. doi: 10.3390/v6020893. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 24553111 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The matrix metalloproteinase ADAM10 supports hepatitis C virus entry and cell-to-cell spread via its sheddase activity.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Nov 15;19(11):e1011759. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011759. eCollection 2023 Nov. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37967063 Free PMC article.
-
The ACE2 Receptor for Coronavirus Entry Is Localized at Apical Cell-Cell Junctions of Epithelial Cells.Cells. 2022 Feb 11;11(4):627. doi: 10.3390/cells11040627. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35203278 Free PMC article.
-
HPV16 Entry into Epithelial Cells: Running a Gauntlet.Viruses. 2021 Dec 8;13(12):2460. doi: 10.3390/v13122460. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34960729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Abl2 Kinase Regulate Distinct Steps of Human Papillomavirus 16 Endocytosis.J Virol. 2020 May 18;94(11):e02143-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02143-19. Print 2020 May 18. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32188731 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of epithelial growth factor receptors by the oncoprotein E5 during the HPV16 differentiation-dependent life cycle.Tumour Virus Res. 2025 Jun;19:200315. doi: 10.1016/j.tvr.2025.200315. Epub 2025 Mar 7. Tumour Virus Res. 2025. PMID: 40057277 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

