What Are the Uses and Limitations of Time-driven Activity-based Costing in Total Joint Replacement?
- PMID: 31107316
- PMCID: PMC7000080
- DOI: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000765
What Are the Uses and Limitations of Time-driven Activity-based Costing in Total Joint Replacement?
Abstract
Background: With increasing emphasis on value-based payment models for primary total joint arthroplasty (TJA), there is greater need for orthopaedic surgeons and hospitals to better understand the actual costs and resource use of TJA. Time-driven activity-based costing (TDABC) is a methodology for accurate cost estimation, but its application in the TJA care pathway across institutions/regions has not yet been analyzed.
Questions/purposes: In this systematic review of studies applying TDABC to primary TJA, we investigated the following: (1) Is there variation in TDABC methodology and cost estimates across institutions? (2) Is a standard set of direct and indirect costs included across studies? (3) Is there a difference in cost estimates derived from TDABC and traditional hospital cost-accounting approaches? and (4) How are institutions using TDABC (process and outputs) with respect to the TJA care pathway?
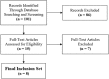
Methods: A comprehensive search strategy was developed that included the keywords "TDABC," "time-driven activity-based cost," "THA," "TKA," "THR," "TKR," and "TJR" in the PubMed/MEDLINE, EMBASE, Web of Science, Ovid SP, Scopus, and ScienceDirect databases for articles published between 2004 and 2018 as well as extensive hand searching and citation mining. Relevant studies (n = 15) were screened to include THA or TKA as the focus of the TDABC model, full-text articles, TDABC-based cost estimates for TJA, and studies written in English (n = 8). Due to the heterogeneity of outcomes/methodology in TDABC studies involving TJA, quality assessment was based on each study's adherence to the seven steps delineated by Kaplan et al. in their original publication introducing TDABC in health care.
Results: There was substantial variation in TDABC methodology (especially in scope), adherence to the seven steps of TDABC, and data collection. Only five of eight studies incorporated indirect costs into their TDABC calculation, with notable differences in which direct and indirect expenses were included. TDABC-based cost estimates for TJA ranged from USD 7081 to USD 29,557, with variation driven by the TJA timeframe and whether implant costs were included in the costing calculation. TDABC was most frequently used to compare against traditional hospital accounting methods (n = 4), to increase operational efficiency (n = 4), to reduce wasted resources (n = 3), and to mitigate risk (n = 3).
Conclusions: TDABC-based cost estimates are more granular and useful in practice than those calculated via traditional hospital accounting; however, there is a lack of standardized principles to guide TDABC implementation (especially for indirect costs) due to institutional and regional differences in TDABC application. Although TDABC methodology will likely continue to vary somewhat between studies, standardized principles are needed to guide the definition, estimation, and reporting of costs to enable detailed examination of study methodology and inputs by readers.
Level of evidence: Level III, economic and decision analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Each author certifies that neither he or she, nor any member of his or her immediate family, have funding or commercial associations (consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and
Figures
Comment in
-
CORR Insights®: What Are the Uses and Limitations of Time-driven Activity-based Costing in Total Joint Replacement?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019 Sep;477(9):2082-2084. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000812. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019. PMID: 31135542 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Andreasen SE, Holm HB, Jorgensen M, Gromov K, Kjaersgaard-Andersen P, Husted H. Time-driven activity-based cost of fast-track total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32:1747-1755. - PubMed
-
- Chen A, Sabharwal S, Akhtar K, Makaram N, Gupte CM. Time-driven activity based costing of total knee replacement surgery at a London teaching hospital. Knee. 2015;22:640-645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

