Handling stress impairs learning through a mechanism involving caspase-1 activation and adenosine signaling
- PMID: 31108171
- PMCID: PMC6664453
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.05.025
Handling stress impairs learning through a mechanism involving caspase-1 activation and adenosine signaling
Abstract
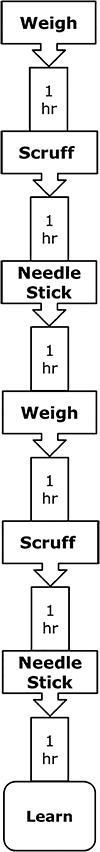
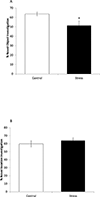
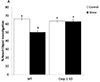
Acute stressors can induce fear and physiologic responses that prepare the body to protect from danger. A key component of this response is immune system readiness. In particular, inflammasome activation appears critical to linking stress to the immune system. Here, we show that a novel combination of handling procedures used regularly in mouse research impairs novel object recognition (NOR) and activates caspase-1 in the amygdala. In male mice, this handling-stress paradigm combined weighing, scruffing and sham abdominal injection once per hr. While one round of weigh/scruff/needle-stick had no impact on NOR, two rounds compromised NOR without impacting location memory or anxiety-like behaviors. Caspase-1 knockout (KO), IL-1 receptor 1 (IL-1R1) KO and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-RA)-administered mice were resistant to handling stress-induced loss of NOR. In addition, examination of the brain showed that handling stress increased caspase-1 activity 85% in the amygdala without impacting hippocampal caspase-1 activity. To delineate danger signals relevant to handling stress, caffeine-administered and adenosine 2A receptor (A2AR) KO mice were tested and found resistant to impaired learning and caspase-1 activation. Finally, mice treated with the β-adrenergic receptor antagonist, propranolol, were resistant to handling stress-induced loss of NOR and caspase-1 activation. Taken together, these results indicate that handling stress-induced impairment of object learning is reliant on a pathway requiring A2AR-dependent activation of caspase-1 in the amygdala that appears contingent on β-adrenergic receptor functionality.
Keywords: Adenosine; Amygdala; Caffeine; Caspase-1; Learning; Stress; β-Adrenergic receptor.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures















Similar articles
-
HFD refeeding in mice after fasting impairs learning by activating caspase-1 in the brain.Metabolism. 2020 Jan;102:153989. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2019.153989. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Metabolism. 2020. PMID: 31697963 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia/reoxygenation impairs memory formation via adenosine-dependent activation of caspase 1.J Neurosci. 2012 Oct 3;32(40):13945-55. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0704-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23035103 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine through the A2A adenosine receptor increases IL-1β in the brain contributing to anxiety.Brain Behav Immun. 2014 Oct;41:218-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.05.018. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Brain Behav Immun. 2014. PMID: 24907587 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1 receptor antagonist ameliorates inflammasome-dependent alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice.J Clin Invest. 2012 Oct;122(10):3476-89. doi: 10.1172/JCI60777. Epub 2012 Sep 4. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22945633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The intersection of cell death and inflammasome activation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Jun;73(11-12):2349-67. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2205-2. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27066895 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mouse Testing Methods in Psychoneuroimmunology: Measuring Behavioral Responses.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2868:163-203. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4200-9_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39546231
-
HFD refeeding in mice after fasting impairs learning by activating caspase-1 in the brain.Metabolism. 2020 Jan;102:153989. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2019.153989. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Metabolism. 2020. PMID: 31697963 Free PMC article.
-
Gut dysbiosis-induced vitamin B6 metabolic disorder contributes to chronic stress-related abnormal behaviors in a cortisol-independent manner.Gut Microbes. 2025 Dec;17(1):2447824. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2447824. Epub 2025 Jan 7. Gut Microbes. 2025. PMID: 39773070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AHA hospital statistics, 2017. Health Forum LLC.
-
- Ambrogi Lorenzini C, Bucherelli C, Giachetti A, Tassoni G, 1987. Spontaneous and conditioned behavior of Wistar and Long Evans rats. Arch. Ital. Biol 125, 155–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

