Microstructural neuroimaging of white matter tracts in persistent post-concussion syndrome: A prospective controlled cohort study
- PMID: 31108457
- PMCID: PMC6526293
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101842
Microstructural neuroimaging of white matter tracts in persistent post-concussion syndrome: A prospective controlled cohort study
Abstract
Introduction: Children with mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) typically recover quickly, however approximately 15% experience persistent post-concussive symptoms (PPCS) past 3 months. The microstructural pathology associated with underlying persistent symptoms is poorly understood but is suggested to involve axonal injury to white matter tracts. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) can be used to visualize and characterize damage to white matter microstructure of the brain.
Objective: We aimed to investigate white matter microstructure in children with persistent concussive symptoms as compared to typically developing controls, alongside evaluating differences in white matter changes over time and how this relates to symptom recovery.
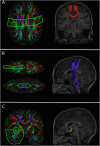
Methods: The current study is a prospective, longitudinal, controlled cohort study of children with mTBI. 104 children aged 8 to 18 years with a mTBI (72 symptomatic; 32 asymptomatic) were recruited from the Alberta Children's Hospital and compared to 20 healthy controls. Microstructural evidence of white matter injury was evaluated using DTI one month post injury and repeated 4 to 6 weeks later. Primary outcomes included fractional anisotropy and mean diffusivity of the corticospinal tracts, uncinate fasciculi, and motor fibers of the corpus callosum. Post-concussive symptoms were also measured using the Post-Concussion Symptom Inventory (PCSI) taken at both time points.
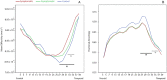
Results: Fractional anisotropy of the left uncinate fasciculi was lower in symptomatic children compared to controls (F(2,119) = 3.582, p = 0.031). No other significant differences were observed.
Conclusions: Our findings provide evidence of microstructural injury following mTBI in children with ongoing post-concussive symptoms one month post injury. The changes were persistent 4-6 weeks later. Further longitudinal studies of white matter microstructure in PPCS will be helpful to clarify whether these white matter alterations resolve over time.
Keywords: Diffusion tensor imaging; Mild traumatic brain injury; Pediatrics; Persistent post-concussive symptoms; Uncinate fasciculus.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Adams H., Mitchell D.E., Graham D.I., Doyle D. Diffuse brain damage of immediate impact type. Its relationship to'primary brain-stem damage'in head injury. Brain. 1977;100(3):489–502. - PubMed
-
- Adams J.H., Doyle D., Ford I., Gennarelli T.A., Graham D.I., McLellan D.R. Diffuse axonal injury in head injury: definition, diagnosis and grading. Histopathol. 1989;15(1):49–59. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong R.C., Mierzwa A.J., Marion C.M., Sullivan G.M. White matter involvement after TBI: clues to axon and myelin repair capacity. Exp. Neurol. 2016;275:328–333. - PubMed
-
- Barlow K.M., Crawford S., Stevenson A., Sandhu S.S., Belanger F., Dewey D. Epidemiology of postconcussion syndrome in pediatric mild traumatic brain injury. Pediatr. 2010;126(2):e374. (peds-2009) - PubMed
-
- Barlow K.M., Brooks B.L., MacMaster F.P., Kirton A., Seeger T., Esser M.…Kirk V. A double-blind, placebo-controlled intervention trial of 3 and 10 mg sublingual melatonin for post-concussion syndrome in youths (PLAYGAME): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2014;15(1):271. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

