IL-1 beta-mediated macrophage-hepatocyte crosstalk upregulates hepcidin under physiological low oxygen levels
- PMID: 31108461
- PMCID: PMC6526398
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101209
IL-1 beta-mediated macrophage-hepatocyte crosstalk upregulates hepcidin under physiological low oxygen levels
Abstract
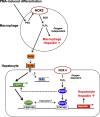
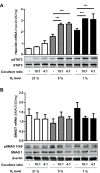
In mammals, the iron masterswitch hepcidin efficiently controls iron recycling by the macrophage-liver axis but the exact interplay between macrophages and hepatocytes remains poorly understood. We here study hepcidin response during macrophage differentiation as well as the macrophage-hepatocyte crosstalk and its subsequent effects on hepatocyte hepcidin using an in vitro co-culture model that mimics the physiological liver microenvironment. We show that macrophage differentiation strongly induces hepcidin by 60-fold both in THP1 macrophages and primary isolated monocyte-derived macrophages. Removal of H2O2 by catalase or inhibition of NOX2 efficiently blocked hepcidin induction. After differentiation, macrophage hepcidin accounted for 10% of total hepatocyte hepcidin and did not respond to low oxygen levels. In contrast, co-culture of differentiated macrophages with Huh7 cells significantly induced hepatocyte hepcidin, which was further potentiated under low oxygen levels. Hepatocyte hepcidin was also upregulated when Huh7 cells were solely exposed to macrophage-conditioned hypoxic medium. A cytokine screen identified macrophage secreted IL-1β as major inducer of hepcidin in hepatocytes. In confirmation, treatment of Huh7 cells with the IL-1 receptor antagonist (anakinra) completely blunted macrophage-mediated hepcidin transcription in hepatocytes. Finally, detailed analysis of potentially involved signaling pathways points toward STAT3 and CEBPδ-mediated hepcidin induction independent of IL-6. In conclusion, our study demonstrates a strong NOX2-mediated hepcidin induction during macrophage differentiation. These differentiated macrophages are able to efficiently induce hepatocyte hepcidin mainly through secretion of IL-1β. Our data highlight a hitherto unrecognized role of macrophage-hepatocyte crosstalk for a joint and oxygen-dependent hepcidin production through STAT3 and CEBPδ.
Keywords: Cytokines; Hydrogen peroxide; Hypoxia; Iron metabolism/hepcidin; NADPH oxidase; STAT3.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Krause A., Neitz S., Magert H.J., Schulz A., Forssmann W.G., Schulz-Knappe P., Adermann K. LEAP-1, a novel highly disulfide-bonded human peptide, exhibits antimicrobial activity. FEBS Lett. 2000;480(2–3):147–150. - PubMed
- A. Krause, S. Neitz, H.J. Magert, A. Schulz, W.G. Forssmann, P. Schulz-Knappe, K. Adermann, LEAP-1, a novel highly disulfide-bonded human peptide, exhibits antimicrobial activity, FEBS Lett 480(2-3) (2000) 147-150. - PubMed
-
- Park C.H., Valore E.V., Waring A.J., Ganz T. Hepcidin, a urinary antimicrobial peptide synthesized in the liver. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276(11):7806–7810. - PubMed
- C.H. Park, E.V. Valore, A.J. Waring, T. Ganz, Hepcidin, a urinary antimicrobial peptide synthesized in the liver, J Biol Chem 276(11) (2001) 7806-7810. - PubMed
-
- Sow F.B., Florence W.C., Satoskar A.R., Schlesinger L.S., Zwilling B.S., Lafuse W.P. Expression and localization of hepcidin in macrophages: a role in host defense against tuberculosis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007;82(4):934–945. - PubMed
- F.B. Sow, W.C. Florence, A.R. Satoskar, L.S. Schlesinger, B.S. Zwilling, W.P. Lafuse, Expression and localization of hepcidin in macrophages: a role in host defense against tuberculosis, J Leukoc Biol 82(4) (2007) 934-945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

