Comprehensive Eutrophication Assessment Based on Fuzzy Matter Element Model and Monte Carlo-Triangular Fuzzy Numbers Approach
- PMID: 31109129
- PMCID: PMC6572366
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16101769
Comprehensive Eutrophication Assessment Based on Fuzzy Matter Element Model and Monte Carlo-Triangular Fuzzy Numbers Approach
Abstract
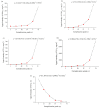
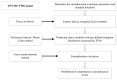
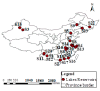
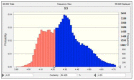
Evaluating the eutrophication level of lakes with a single method alone is challenging since uncertain, fuzzy, and complex processes exist in eutrophication evaluations. The parameters selected for assessing eutrophication include chlorophyII-a, chemical oxygen demand, total phosphorus, total nitrogen, and clarity. Firstly, to deal with the uncertainties and fuzziness of data, triangular fuzzy numbers (TFN) were applied to describe the fuzziness of parameters. Secondly, to assess the eutrophication grade of lakes comprehensively, an improved fuzzy matter element (FME) approach was incorporated with TFNs with weights determined by combination of entropy method and analytic hierarchy process (AHP). In addition, the Monte Carlo (MC) approach was applied to easily simulate the arithmetic operations of eutrophication evaluation. The hybrid model of TFN, FME, and MC method is termed as the TFN⁻MC⁻FME model, which can provide more valuable information for decision makers. The developed model was applied to assess the eutrophication levels of 24 typical lakes in China. The evaluation indicators were expressed by TFNs input into the FME model to evaluate eutrophication grade. The results of MC simulation supplied quantitative information of possible intervals, the corresponding probabilities, as well as the comprehensive eutrophication levels. The eutrophication grades obtained for most lakes were identical to the results of the other three methods, which proved the correctness of the model. The presented methodology can be employed to process the data uncertainties and fuzziness by stochastically simulating their distribution characteristics, and obtain a better understanding of eutrophication levels. Moreover, the proposed model can also describe the trend of eutrophication development in lakes, and provide more valuable information for lake management authorities.
Keywords: Monte Carlo approach; eutrophication evaluation; fuzzy matter element model; triangle fuzzy number.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eutrophication Assessment Based on the Cloud Matter Element Model.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jan 3;17(1):334. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17010334. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 31947780 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic water quality evaluation based on fuzzy matter-element model and functional data analysis, a case study in Poyang Lake.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Aug;24(23):19138-19148. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9371-0. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28660517
-
Approach based on TOPSIS and Monte Carlo simulation methods to evaluate lake eutrophication levels.Water Res. 2020 Dec 15;187:116437. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116437. Epub 2020 Sep 19. Water Res. 2020. PMID: 33002773
-
Development of methods for establishing nutrient criteria in lakes and reservoirs: A review.J Environ Sci (China). 2018 May;67:54-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2017.07.013. Epub 2017 Jul 25. J Environ Sci (China). 2018. PMID: 29778174 Review.
-
A bibliometric review of nitrogen research in eutrophic lakes and reservoirs.J Environ Sci (China). 2018 Apr;66:274-285. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2016.10.022. Epub 2017 May 5. J Environ Sci (China). 2018. PMID: 29628095 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Graphene-Based Materials for Detection of Nitrate and Nitrite in Water-A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Dec 20;20(1):54. doi: 10.3390/s20010054. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31861855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eutrophication Assessment Based on the Cloud Matter Element Model.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jan 3;17(1):334. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17010334. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 31947780 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of River Water Quality Based on an Improved Fuzzy Matter-Element Model.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Aug 5;16(15):2793. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16152793. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31387258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li B., Yang G., Wan R., Hörmann G., Huang J., Fohrer N., Zhang L. Combining multivariate statistical techniques and random forests model to assess and diagnose the trophic status of Poyang Lake in China. Ecol. Indic. 2017;83:74–83. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.07.033. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

