β-Caryophyllene as a Potential Protective Agent Against Myocardial Injury: The Role of Toll-Like Receptors
- PMID: 31109132
- PMCID: PMC6572120
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24101929
β-Caryophyllene as a Potential Protective Agent Against Myocardial Injury: The Role of Toll-Like Receptors
Abstract
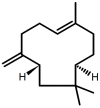
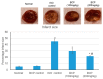
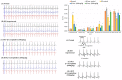
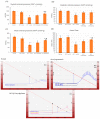
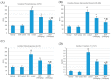
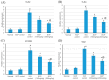
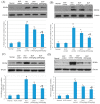
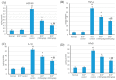
Myocardial infarction (MI) remains one of the major causes of mortality around the world. A possible mechanism involved in myocardial infarction is the engagement of Toll-like receptors (TLRs). This study was intended to discover the prospective cardioprotective actions of β-caryophyllene, a natural sesquiterpene, to ameliorate isoproterenol (ISO)-induced myocardial infarction through HSP-60/TLR/MyD88/NFκB pathway. β-Caryophyllene (100 or 200 mg/kg/day orally) was administered for 21 days then MI was induced via ISO (85 mg/kg, subcutaneous) on 20th and 21st days. The results indicated that ISO induced a significant infarcted area associated with several alterations in the electrocardiogram (ECG) and blood pressure (BP) indices and caused an increase in numerous cardiac indicators such as creatine phosphokinase (CPK), creatine kinase-myocardial bound (CK-MB), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and cardiac tropinine T (cTnT). In addition, ISO significantly amplified heat shock protein 60 (HSP-60) and other inflammatory markers, such as TNF-α, IL-Iβ, and NFκB, and affected TLR2 and TLR4 expression and their adaptor proteins; Myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MYD88), and TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β (TRIF). On the other hand, consumption of β-caryophyllene significantly reversed the infarcted size, ECG and BP alterations, ameliorated the ISO elevation in cardiac indicators; it also notably diminished HSP-60, and subsequently TLR2, TLR4, MYD88, and TRIF expression, with a substantial reduction in inflammatory mediator levels. This study revealed the cardioprotective effect of β-caryophyllene against MI through inhibiting HSP-60/TLR/MyD88/NFκB signaling pathways.
Keywords: MyD88; heat shock protein 60; isoproterenol; toll-like receptors; β-caryophyllene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The sponsor body has no role in study design; in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the article for publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Norisoboldine Alleviates Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Ischemic Injury via the TLR4-MyD88-Dependent NF-κB Activation Pathway and Modulation of L-Type Calcium Channels.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2025 Apr;52(4):e70033. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.70033. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40011076
-
Cutting edge: a novel Toll/IL-1 receptor domain-containing adapter that preferentially activates the IFN-beta promoter in the Toll-like receptor signaling.J Immunol. 2002 Dec 15;169(12):6668-72. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.12.6668. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12471095
-
Gentianella acuta prevents acute myocardial infarction induced by isoproterenol in rats via inhibition of galectin-3/TLR4/MyD88/NF-кB inflammatory signalling.Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Feb;29(1):205-219. doi: 10.1007/s10787-020-00708-4. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 32356088
-
Modulation of Toll-interleukin 1 receptor mediated signaling.J Mol Med (Berl). 2005 Apr;83(4):258-66. doi: 10.1007/s00109-004-0622-4. Epub 2005 Jan 21. J Mol Med (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15662540 Review.
-
TLR signaling pathways.Semin Immunol. 2004 Feb;16(1):3-9. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2003.10.003. Semin Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14751757 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-Target Effects of ß-Caryophyllene and Carnosic Acid at the Crossroads of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neurodegeneration: From Oxidative Stress to Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 18;11(6):1199. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061199. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Chaperonin HSP60: Current Understanding and Future Prospects.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 17;25(10):5483. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105483. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-Caryophyllene, A Natural Dietary CB2 Receptor Selective Cannabinoid can be a Candidate to Target the Trinity of Infection, Immunity, and Inflammation in COVID-19.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 14;12:590201. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.590201. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34054510 Free PMC article.
-
Terpenoids as Potential Geroprotectors.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Jun 17;9(6):529. doi: 10.3390/antiox9060529. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32560451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Protective Effect of Anethole against Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion: The Role of the TLR2,4/MYD88/NFκB Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Mar 11;11(3):535. doi: 10.3390/antiox11030535. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Srivastava R.A., Pinkosky S.L., Filippov S., Hanselman J.C., Cramer C.T., Newton R.S. AMP-activated protein kinase: An emerging drug target to regulate imbalances in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism to treat cardio-metabolic diseases. J. Lipid Res. 2012;5312:2490–2514. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R025882. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

