RNA-seq data reveals a coordinated regulation mechanism of multigenes involved in the high accumulation of palmitoleic acid and oil in sea buckthorn berry pulp
- PMID: 31109294
- PMCID: PMC6528223
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-019-1815-x
RNA-seq data reveals a coordinated regulation mechanism of multigenes involved in the high accumulation of palmitoleic acid and oil in sea buckthorn berry pulp
Abstract
Background: Sea buckthorn is a woody oil crop in which palmitoleic acid (C16:1n7, an omega-7 fatty acid (FA)) contributes approximately 40% of the total FA content in berry pulp (non-seed tissue). However, the molecular mechanisms contributing to the high accumulation of C16:1n7 in developing sea buckthorn berry pulp (SBP) remain poorly understood.
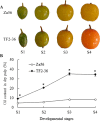
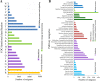
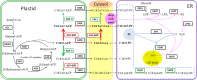
Results: We identified 1737 unigenes associated with lipid metabolism through RNA-sequencing analysis of the four developmental stages of berry pulp in two sea buckthorn lines, 'Za56' and 'TF2-36'; 139 differentially expressed genes were detected between the different berry pulp developmental stages in the two lines. Analyses of the FA composition showed that the C16:1n7 contents were significantly higher in line 'Za56' than in line 'TF2-36' in the mid-late developmental stages of SBP. Additionally, qRT-PCR analyses of 15 genes involved in FA and triacylglycerol (TAG) biosynthesis in both lines revealed that delta9-ACP-desaturase (ACP-Δ9D) competed with 3-ketoacyl-ACP-synthase II (KASII) for the substrate C16:0-ACP and that ACP-Δ9D and delta9-CoA-desaturase (CoA-Δ9D) gene expression positively correlated with C16:1n7 content; KASII and fatty acid elongation 1 (FAE1) gene expression positively correlated with C18:0 content in developing SBP. Specifically, the abundance of ACP-Δ9D and CoA-Δ9D transcripts in line 'Za56', which had a higher C16:1n7 content than line 'TF2-36', suggests that these two genes play an important role in C16:1n7 biosynthesis. Furthermore, the high expressions of the glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPD1) gene and the WRINKLED1 (WRI1) transcription factor contributed to increased biosynthesis of TAG precursor and FAs, respectively, in the early developmental stages of SBP, and the high expression of the diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1) gene increased TAG assembly in the later developmental stages of SBP. Overall, we concluded that increased ACP-Δ9D and CoA-Δ9D levels coupled with decreased KASII and FAE1 activity is a critical event for high C16:1n7 accumulation and that the coordinated high expression of WRI1, GPD1, and DGAT1 genes resulted in high oil accumulation in SBP.
Conclusion: Our results provide a scientific basis for understanding the mechanism of high C16:1n7 accumulation in berry pulp (non-seed tissue) and are valuable to the genetic breeding programme for achieving a high quality and yield of SBP oil.
Keywords: Berry pulp oil; Fatty acid biosynthesis; Hippophae L.; Non-seed tissue; Oil accumulation; Palmitoleic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Nontargeted metabolomic and multigene expression analyses reveal the mechanism of oil biosynthesis in sea buckthorn berry pulp rich in palmitoleic acid.Food Chem. 2022 Apr 16;374:131719. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131719. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 34875440
-
Tandem Mass Tag Based Quantitative Proteomics of Developing Sea Buckthorn Berries Reveals Candidate Proteins Related to Lipid Metabolism.J Proteome Res. 2019 May 3;18(5):1958-1969. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00764. Epub 2019 Apr 23. J Proteome Res. 2019. PMID: 30990047
-
Fatty acid composition of developing sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) berry and the transcriptome of the mature seed.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034099. Epub 2012 Apr 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22558083 Free PMC article.
-
Abundance of active ingredients in sea-buckthorn oil.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 May 19;16(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0469-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28526097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The comprehensive regulatory network in seed oil biosynthesis.J Integr Plant Biol. 2025 Mar;67(3):649-668. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13834. Epub 2025 Jan 17. J Integr Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39821491 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of Hub Genes Involved in Seed Development and Lipid Biosynthesis in Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) Using UID Transcriptome Sequencing.Plants (Basel). 2025 Aug 6;14(15):2436. doi: 10.3390/plants14152436. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805785 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity of Hippophae rhamnoides varieties with different fruit characteristics based on whole-genome sequencing.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Mar 4;16:1542552. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1542552. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40104038 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Characterization of a Novel Acyl-ACP Δ9 Desaturase Gene Responsible for Palmitoleic Acid Accumulation in a Diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum.Front Microbiol. 2020 Dec 16;11:584589. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.584589. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33391203 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the key flavonoid and lipid synthesis proteins in the pulp of two sea buckthorn cultivars at different developmental stages.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Jun 17;22(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03688-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35710338 Free PMC article.
-
The Systematics, Reproductive Biology, Biochemistry, and Breeding of Sea Buckthorn-A Review.Genes (Basel). 2023 Nov 24;14(12):2120. doi: 10.3390/genes14122120. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136942 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ruan CJ, Rumpunen K, Nybom H. Advances in improvement of quality and resistance in a multipurpose crop: sea buckthorn. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2013;33(2):126–144. - PubMed
-
- Ding J, Ruan CJ, Guan Y, Shan JY. Comparison of oil contents and fatty acid composition between developing sea buckthorn pulp and seed. China Oil and Fats. 2017;42(5):140–144.
-
- Yang B, Kallio H. Fatty acid composition of lipids in sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) berries of different origins. J Agric Food Chem. 2001;49(4):1939–1947. - PubMed
-
- Li W, Ruan CJ, Teixeira da Silva JA, Guo H, Zhao CE. NMR metabolomics of berry quality in sea buckthorn (Hippophae L.) Mol Breeding. 2013;31(1):57–67.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

