[Characteristics of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor with Rare Mutations in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and the Effect of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on Them]
- PMID: 31109439
- PMCID: PMC6533192
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2019.05.06
[Characteristics of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor with Rare Mutations in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and the Effect of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on Them]
Abstract
Background: Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of lung cancer. It has been clinically evaluated that therapiestargeting against the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) as the clinical standard first-line treatment. The response and outcome of EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in patients harboring common mutations in EGFR kinase domain (deletion in exon19 and L858R in exon 21) has been well demonstrated, but not in rare or complex mutations.
Methods: A total of 150 patients that harbored rare or complex mutations in EGFR diagnosed by histopathology were included in this retrospective study. The clinical-pathological characteristics of all 150 patients as well as the response and progression-free survival (PFS) in 48 patients that received EGFR-TKIs in first/second/third line treatments weredescribed and analyzed.
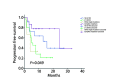
Results: Patients were divided into four groups based on the mutation types: single G719X point mutation in exon 18 (n=46, 30.7%), single L861Q point mutation in exon 21 (n=45, 30.0%), other single rare mutation (n=14, 9.3%) and complex mutations (n=45, 30.0%). The result indicated thatthere was no correlation of EGFR mutation typeswith other parameters such as gender, age, clinical stage, pathology and smoking history. For the 48 patients that received EGFR-TKIs treatment, there were no significant differencesamong 4 groups in terms of objective response rate (ORR) and disease control rate (DCR) (54.5% vs 30.0% vs 0.0% vs 35.7%, χ²=3.200, P=0.34; 90.9% vs 85.0% vs 66.7% vs 92.9%, χ²=2.162, P=0.59). The median progress-free survival (mPFS) was 11.0 months (95%CI: 4.4-17.6), and in each group of different EGFR mutation types are 15.8 months (95%CI: 9.5-22.2), 8.0 months (95%CI: 5.1-11.0), 4.9 months (95%CI: 1.4-8.4) and 23.1 months (95%CI: 15.8-30.4)(χ²=7.876, P=0.049).
Conclusions: The efficiency of targeting EGFR-TKIs on different types of rare or complex mutations was heterogeneous. The PFS may be better in patients that harbored complex mutations than those with single rare mutations. Further studies with larger sample size are necessary. Moreover, to discover novel therapeutic targets and develop new drugs are imminentfor those patientswith no response to the existing treatments.
【中文题目:EGFR基因少见突变型非小细胞肺癌的临床 特征及应用EGFR-TKIs治疗效果评价】 【中文摘要:背景与目的 晚肺腺癌是肺癌中最常见的类型,表皮生长因子受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors, EGFR-TKIs)目前已成为EGFR突变型非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer, NSCLC)的一线标准治疗。经典型突变(19外显子缺失突变和21外显子L858R突变)应用EGFR-TKIs治疗的效果已有大量研究和报道,而少见或复合突变类型的相关报道较少,具体疗效尚未完全统一定论。方法 对2016年8月-2018年4月就诊于郑州大学第一附属医院的150例经基因检测证实为EGFR少见突变的NSCLC患者进行回顾性研究,分析其突变类型及临床病理特征,并对其中48例接受EGFR-TKIs I/II/III线治疗的患者的疗效进行描述和评价。结果 将全部150例患者按突变类型分为4组,分别为18外显子G719X突变46例(30.7%)、21外显子L861Q突变45例(30.0%)、其他单一少见突变14例(9.3%)和复合突变45例(30%)。EGFR基因少见或复合突变类型与性别、年龄、分期、病理类型及吸烟史均无关。对于48例接受EGFR-TKIs治疗的患者,4组不同类型突变的患者客观缓解率(objective response rate, ORR)和疾病控制率(disease control rate, DCR)差异无统计学意义(54.5% vs 30.0% vs 0.0% vs 35.7%, χ²=3.200, P=0.34; 90.9% vs 85.0% vs 66.7% vs 92.9%, χ²=2.162, P=0.59)。中位无进展生存期(median progress free survival, mPFS)为11.0个月(95%CI: 4.4-17.6),在EGFR基因突变不同类型分组中分别为[15.8个月(95%CI: 9.5-22.2)、8.0个月(95%CI: 5.1-11.0)、4.9个月(95%CI: 1.4-8.4)、23.1个月(95%CI: 15.8-30.4)](χ²=7.876, P=0.049)。结论不同类型的EGFR少见或复合突变类型应用EGFR的疗效不尽相同,复合突变组PFS可能优于单一少见突变组。接下来有必要进一步进行大样本量的研究,发现新的敏感靶点和研究新一代的药物对于接受现有治疗效果欠佳的患者也是值得期待的。】 【中文关键词:肺肿瘤;EGFR;突变;靶向治疗;EGFR-TKIs】.
Keywords: EGFR; EGFR-TKIs; Lung neoplasms; Mutation; Target therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring different types of EGFR mutations: A retrospective analysis.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017 Dec;37(6):864-872. doi: 10.1007/s11596-017-1819-4. Epub 2017 Dec 21. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29270745
-
Effectiveness of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Japanese Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Minor Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutations: Results from a Multicenter Retrospective Study (HANSHIN Oncology Group 0212).Anticancer Res. 2015 Jul;35(7):3885-91. Anticancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26124334
-
First-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in 106 patients with compound EGFR-mutated lung cancer: a single institution's clinical practice experience.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2018 Jul 28;38(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s40880-018-0321-0. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2018. PMID: 30055651 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review of uncommon EGFR mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2017 Dec;114:96-102. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Lung Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29173773 Review.
-
Heterogeneous Responses to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) in Patients with Uncommon EGFR Mutations: New Insights and Future Perspectives in this Complex Clinical Scenario.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 21;20(6):1431. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061431. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30901844 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous