[Prognostic Analysis of EGFR-TKIs Combined with Gamma Knife in EGFR-mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma with Brain Metastasis]
- PMID: 31109441
- PMCID: PMC6533187
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2019.05.08
[Prognostic Analysis of EGFR-TKIs Combined with Gamma Knife in EGFR-mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma with Brain Metastasis]
Abstract
Background: Advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant lung adenocarcinoma had a high overall incidence of brain metastasis during the full course, and local brain radiotherapy combined with systemic targeted therapy may be a better strategy. This study aimed to identify the prognostic factors of EGFR-mutant brain-metastatic lung adenocarcinoma patients who received EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) in combination with gamma knife radiosurgery.
Methods: Retrospective analysis of EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma patients with brain metastases which developed at initial diagnosis or during EGFR-TKIs treatment period were performed. Intracranial progression free survival (PFS) was statistically analyzed between different subgroups to find out the prognostic factors including gender, age, smoking history, extracranial metastasis, EGFR mutation type, size and number of intracranial lesions, carcino-embryonic antigen (CEA) level, lung-molGPA score and so on.
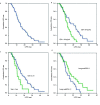
Results: A total of 74 EGFR-mutant brain-metastatic lung adenocarcinoma patients were enrolled in this study, with median intracranial PFS of 14.7 months. One-year intracranial-progression-free rate was 58.5%, and two-year rate was 22.2%. Univariate survival analysis showed that patients with lower CEA level at initial diagnosis (<10 ng/L)(16.9 months vs 12.6 months, P=0.012) and smaller intracranial lesions (<2 cm)(15.4 months vs 10.8 months, P=0.021) and higher lung-molGPA score (>3)(15 months vs 12.6 months, P=0.041) were prone to have a superior intracranial PFS. Multivariate analysis showed that CEA≥10 ng/mL and intracranial lesion≥2 cm were the independent risk factors of intracranial PFS.
Conclusions: EGFR-TKIs in combination with gamma knife radiosurgery was an efficient treatment option to control the cranial tumor lesion. CEA≥10 μg/L at initial diagnosis and intracranial lesion≥2 cm were the risk factors of EGFR-mutant brain-metastatic lung adenocarcinoma patients receiving EGFR-TKIs in combination with gamma knife radiosurgery.
【中文题目:EGFR-TKIs联合伽玛刀治疗EGFR突变的肺腺癌伴脑转移的预后分析】 【中文摘要:背景与目的 晚期表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR)基因突变的肺腺癌在初诊或治疗过程中脑转移的总发生率高,局部治疗联合系统性靶向治疗可能是更佳策略。本研究拟探讨分析EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(tyrosine kinase inhibitors, TKIs)联合头颅伽玛刀治疗EGFR突变的肺腺癌伴脑转移患者的疗效及预后因素。方法 回顾性收集EGFR基因突变的肺腺癌、在初诊即存在脑转移或在EGFR-TKIs治疗过程中肺部病灶稳定而出现脑转移、接受一线口服EGFR-TKIs靶向治疗联合脑部伽玛刀局部治疗的患者,评价EGFR-TKIs联合头颅伽马刀治疗对颅内病灶的疗效,随访并分析颅内无进展生存时间(intracranial progression free survival, i-PFS),探索EGFR突变肺腺癌伴脑转移的预后因素。结果 共纳入74例患者,其中位i-PFS为14.7个月,1年无颅内进展率为58.5%,2年无颅内进展率为22.2%。颅内病灶与肺部病灶具有相近的进展时间。单因素生存分析显示,初诊癌胚抗原(carcinoembryonic antigen, CEA)水平<10 ng/mL(16.9个月vs 12.6个月,P=0.012)、颅内病灶长径<2 cm(15.4个月 vs 10.8个月,P=0.021)、肺癌脑转移分级预后系统(lung graded prognostic assessment, Lung-molGPA)评分>3(15个月 vs 12.6个月,P=0.041)的患者具有更长的i-PFS。多因素分析显示初诊时CEA≥10 ng/mL和颅内病灶≥2 cm是i-PFS的不良预后因素。结论 EGFR-TKIs联合伽玛刀局部治疗对EGFR突变肺腺癌伴脑转移患者的颅内病灶具有良好的疗效。初诊时CEA水平≥10 ng/mL、颅内病灶≥2 cm是接受EGFR-TKIs联合伽马刀治疗的脑转移肺腺癌患者的不良预后因素。】 【中文关键词:表皮生长因子受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂;伽玛刀;肺腺癌;脑转移;预后因素】.
Keywords: Brain metastasis; Epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI); Gamma knife radiosurgery; Lung adenocarcinoma; Prognostic factors.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous