Tubular cell and keratinocyte single-cell transcriptomics applied to lupus nephritis reveal type I IFN and fibrosis relevant pathways
- PMID: 31110316
- PMCID: PMC6584054
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-019-0386-1
Tubular cell and keratinocyte single-cell transcriptomics applied to lupus nephritis reveal type I IFN and fibrosis relevant pathways
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Tubular cell and keratinocyte single-cell transcriptomics applied to lupus nephritis reveal type I IFN and fibrosis relevant pathways.Nat Immunol. 2019 Nov;20(11):1556. doi: 10.1038/s41590-019-0529-4. Nat Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31605099 Free PMC article.
Abstract
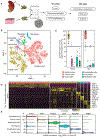
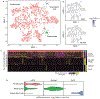
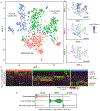
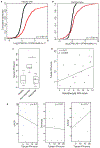
The molecular and cellular processes that lead to renal damage and to the heterogeneity of lupus nephritis (LN) are not well understood. We applied single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) to renal biopsies from patients with LN and evaluated skin biopsies as a potential source of diagnostic and prognostic markers of renal disease. Type I interferon (IFN)-response signatures in tubular cells and keratinocytes distinguished patients with LN from healthy control subjects. Moreover, a high IFN-response signature and fibrotic signature in tubular cells were each associated with failure to respond to treatment. Analysis of tubular cells from patients with proliferative, membranous and mixed LN indicated pathways relevant to inflammation and fibrosis, which offer insight into their histologic differences. In summary, we applied scRNA-seq to LN to deconstruct its heterogeneity and identify novel targets for personalized approaches to therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Single-cell analysis identifies key pathways and prognostic markers in lupus nephritis.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2019 Aug;15(8):457. doi: 10.1038/s41581-019-0164-1. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31164721 No abstract available.
-
Single-cell analysis identifies key pathways and prognostic markers in lupus nephritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019 Jul;15(7):383. doi: 10.1038/s41584-019-0249-z. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31168099 No abstract available.
References
-
- Tsokos GC Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med 365, 2110–2121 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Mohan C & Putterman C Genetics and pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol 11, 329–341 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Weening JJ et al. The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 15, 241–250 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Yu F et al. Tubulointerstitial lesions of patients with lupus nephritis classified by the 2003 International Society of Nephrology and Renal Pathology Society system. Kidney Int. 77, 820–829 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UH2 AR067685/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UM2 AR067678/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003167/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG002295/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067681/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067689/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067690/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067694/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067679/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067688/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AR070582/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG009379/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067677/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067676/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067691/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000371/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

