Culturable hydrocarbonoclastic marine bacterial isolates from Indonesian seawater in the Lombok Strait and Indian Ocean
- PMID: 31111106
- PMCID: PMC6512556
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01594
Culturable hydrocarbonoclastic marine bacterial isolates from Indonesian seawater in the Lombok Strait and Indian Ocean
Abstract
Purpose: The study aims to isolate the culturable marine bacteria and to assess their potential as the bioremediation agent for petroleum hydrocarbons contamination in marine environment.
Methods: Bacteria isolates were obtained by repetitive streaks to obtain purified bacteria on Zobell marine agar plates before further analysis and culture through direct visualization on agar plates. Identification were conducted using 16S rDNA sequence which are compared using NCBI BLAST and, combined with phenotypic and phylogenetic data. The potential use of the selected bacteria was tested by culturing them with two carbon sources i.e., glucose and crude oil.
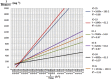
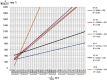
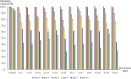
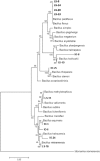
Result: Fifty-one culturable marine hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria were isolated from the Lombok Strait (LS-3, LS-13, LS-14, LS-15, LS-16 and LS-20) and Indian Ocean (IO-1, IO-6, IO-8, IO-19, IO-24 and IO-25). Twelve isolates were found to degrade crude oil efficiently at a >2% concentration and to grow with crude oil as their sole carbon and energy source. These 12 strains belong to the genus Bacillus, which is well known to produce surface active agents, and the oil displacement assay indicated the production of these agents by these strains. Within the genera Bacillus, five species (Bacillus flexus, B. methylotrophicus, B. aquimaris, B. horikoshii, and B. thioparans) were represented by the 12 identified strains.
Conclusion: Selected strains from the Lombok Strait and Indian Ocean were capable of degrading crude oil (2% v/v) by 43.9-71.9% over 14 days. These results are important for marine bioremediation in Indonesia, which often faces risks of oil spill contamination and disaster.
Keywords: Earth sciences; Environmental science; Microbiology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Consistent Occurrence of Hydrocarbonoclastic Marinobacter Strains in Various Cultures of Picocyanobacteria from the Arabian Gulf: Promising Associations for Biodegradation of Marine Oil Pollution.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;26(4):261-8. doi: 10.1159/000445686. Epub 2016 May 12. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27165413
-
[Diversity of oil-degrading bacteria isolated form the Indian Ocean sea surface].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2010 Sep;50(9):1218-25. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2010. PMID: 21090262 Chinese.
-
Isolation, characterization and determination of biotechnological potential of oil-degrading bacteria from Algerian centre coast.J Appl Microbiol. 2019 Mar;126(3):780-795. doi: 10.1111/jam.14185. Epub 2019 Jan 16. J Appl Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30586234
-
Occurrence, production, and export of lipophilic compounds by hydrocarbonoclastic marine bacteria and their potential use to produce bulk chemicals from hydrocarbons.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 May;86(6):1693-706. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2515-5. Epub 2010 Mar 31. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20354694 Review.
-
Petroleum biodegradation in marine environments.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 1999 Aug;1(1):63-70. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 1999. PMID: 10941786 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial biosurfactant increases ex situ biodiesel bioremediation in clayey soil.Biodegradation. 2021 Aug;32(4):389-401. doi: 10.1007/s10532-021-09944-z. Epub 2021 Apr 17. Biodegradation. 2021. PMID: 33864197
-
Microbial Diversity in the Indian Ocean Sediments: An Insight into the Distribution and Associated Factors.Curr Microbiol. 2022 Feb 23;79(4):115. doi: 10.1007/s00284-022-02801-z. Curr Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35195780 Review.
-
Bioaugmentation of Native Fungi, an Efficient Strategy for the Bioremediation of an Aged Industrially Polluted Soil With Heavy Hydrocarbons.Front Microbiol. 2021 Mar 31;12:626436. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.626436. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33868189 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Use of Deep-Sea Sediment Bacteria for Oil Spill Biodegradation: A Laboratory Simulation.Microorganisms. 2022 Aug 10;10(8):1616. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10081616. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36014034 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug-resistant epi-endophytic bacterial community in Posidonia oceanica of Mahdia coast as biomonitoring factor for antibiotic contamination.Arch Microbiol. 2022 Mar 30;204(4):229. doi: 10.1007/s00203-022-02842-9. Arch Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35353264
References
-
- Agogué H., Casamayor E.O., Bourrain M., Obernosterer I., Joux F., Herndl G.J., Lebaron P. A survey on bacteria inhabiting the sea surface microlayer of coastal ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2005;54:269–280. - PubMed
-
- Birch H., Hammershoj R., Comber M., Mayer P. Biodegradation of hydrocarbon mixtures in surface waters at environmentally relevant levels – effect of inoculum origin on kinetics and sequence of degradation. Chemosphere. 2017;184:400–407. - PubMed
-
- Cai Q., Zhu Z., Chen B., Zhang B. Oil-in-water emulsion breaking marine bacteria for demulsifying oily wastewater. Water Res. 2019;149:292–301. - PubMed
-
- Chakraborty R., Wu C.H., Hazen T.C. Systems biology approach to bioremediation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012;23:483–490. - PubMed
-
- Chandankere R., Yao J., Cai M., Masakorala K., Jain A.K., Choi M.M.F. Properties and characterization of biosurfactant in crude oil biodegradation by bacterium Bacillus methylotrophicus USTBa. Fuel. 2014;122:140–148.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

