Distortion-free imaging: A double encoding method (DIADEM) combined with multiband imaging for rapid distortion-free high-resolution diffusion imaging on a compact 3T with high-performance gradients
- PMID: 31111581
- PMCID: PMC6864220
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.26792
Distortion-free imaging: A double encoding method (DIADEM) combined with multiband imaging for rapid distortion-free high-resolution diffusion imaging on a compact 3T with high-performance gradients
Abstract
Background: Distortion-free, high-resolution diffusion imaging using DIADEM (Distortion-free Imaging: A Double Encoding Method), proposed recently, has great potential for clinical applications. However, it can suffer from prolonged scan times and its reliability for quantitative diffusion imaging has not been evaluated.
Purpose: To investigate the clinical feasibility of DIADEM-based high-resolution diffusion imaging on a novel compact 3T (C3T) by evaluating the reliability of quantitative diffusion measurements and utilizing both the high-performance gradients (80 mT/m, 700 T/m/s) and the sequence optimization with the navigator acquisition window reduction and simultaneous multislice (multiband) imaging.
Study type: Prospective feasibility study.
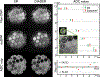
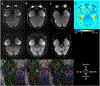
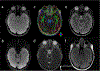
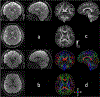
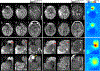
Phantom/subjects: Diffusion quality control phantom scans to evaluate the reliability of quantitative diffusion measurements; 36 normal control scans for B0 -field mapping; six healthy and two patient subject scans with a brain tumor for comparisons of diffusion and anatomical imaging.
Field strength/sequence: 3T; the standard single-shot echo-planar-imaging (EPI), multishot DIADEM diffusion, and anatomical (2D-FSE [fast-spin-echo], 2D-FLAIR [fluid-attenuated-inversion-recovery], and 3D-MPRAGE [magnetization prepared rapid acquisition gradient echo]) imaging.
Assessment: The scan time reduction, the reliability of quantitative diffusion measurements, and the clinical efficacy for high-resolution diffusion imaging in healthy control and brain tumor volunteers.
Statistical test: Bland-Altman analysis.
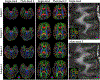
Results: The scan time for high in-plane (0.86 mm2 ) resolution, distortion-free, and whole brain diffusion imaging were reduced from 10 to 5 minutes with the sequence optimizations. All of the mean apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values in phantom were within the 95% confidence interval in the Bland-Altman plot. The proposed acquisition with a total off-resonance coverage of 597.2 Hz wider than the expected bandwidth of 500 Hz in human brain could yield a distortion-free image without foldover artifacts. Compared with EPI, therefore, this approach allowed direct image matching with the anatomical images and enabled improved delineation of the tumor boundaries.
Data conclusion: The proposed high-resolution diffusion imaging approach is clinically feasible on C3T due to a combination of hardware and sequence improvements.
Level of evidence: 3 TECHNICAL EFFICACY: Stage 1 J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020;51:296-310.
Keywords: DIADEM; compact 3T; diffusion imaging; distortion-free; geometric distortion; multishot EPI.
© 2019 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures



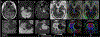
References
-
- Le Bihan D, Breton E. Imagerie de diffusion in-vivo par résonance magnétique nucléaire. Comptes-Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences. 1985;93(5):27–34.
-
- Holodny AI, Ollenschlager M. Diffusion imaging in brain tumors. Neuroimaging Clinics. 2002;12(1):107–124. - PubMed
-
- In MH, Posnansky O, Speck O. High-resolution distortion-free diffusion imaging using hybrid spin-warp and echo-planar PSF-encoding approach. NeuroImage. 2017;148:20–30. - PubMed
-
- Robson MD, Gore JC, Constable RT. Measurement of the point spread function in MRI using constant time imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1997;38(5):733–740. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

