Late-life time-restricted feeding and exercise differentially alter healthspan in obesity
- PMID: 31111669
- PMCID: PMC6612646
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.12966
Late-life time-restricted feeding and exercise differentially alter healthspan in obesity
Abstract
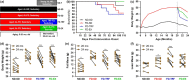
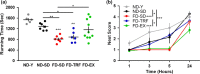
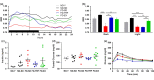
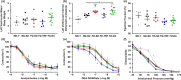
Aging and obesity increase multimorbidity and disability risk, and determining interventions for reversing healthspan decline is a critical public health priority. Exercise and time-restricted feeding (TRF) benefit multiple health parameters when initiated in early life, but their efficacy and safety when initiated at older ages are uncertain. Here, we tested the effects of exercise versus TRF in diet-induced obese, aged mice from 20 to 24 months of age. We characterized healthspan across key domains: body composition, physical, metabolic, and cardiovascular function, activity of daily living (ADL) behavior, and pathology. We demonstrate that both exercise and TRF improved aspects of body composition. Exercise uniquely benefited physical function, and TRF uniquely benefited metabolism, ADL behavior, and circulating indicators of liver pathology. No adverse outcomes were observed in exercised mice, but in contrast, lean mass and cardiovascular maladaptations were observed following TRF. Through a composite index of benefits and risks, we conclude the net healthspan benefits afforded by exercise are more favorable than those of TRF. Extrapolating to obese older adults, exercise is a safe and effective option for healthspan improvement, but additional comprehensive studies are warranted before recommending TRF.
Keywords: aging; exercise; healthspan; obesity; physical activity; time-restricted feeding.
© 2019 The Authors. Aging Cell published by the Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Time-restricted feeding combined with aerobic exercise training can prevent weight gain and improve metabolic disorders in mice fed a high-fat diet.J Physiol. 2022 Feb;600(4):797-813. doi: 10.1113/JP280820. Epub 2021 Jan 26. J Physiol. 2022. PMID: 33450053
-
Short-term time-restricted feeding is safe and feasible in non-obese healthy midlife and older adults.Geroscience. 2020 Apr;42(2):667-686. doi: 10.1007/s11357-020-00156-6. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Geroscience. 2020. PMID: 31975053 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Time-restricted feeding improves insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in a mouse model of postmenopausal obesity.Metabolism. 2016 Dec;65(12):1743-1754. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2016.09.006. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Metabolism. 2016. PMID: 27832862 Free PMC article.
-
A muscle-centric view of time-restricted feeding for older adults.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2021 Nov 1;24(6):521-527. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000789. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2021. PMID: 34475325 Review.
-
Fasting, Circadian Rhythms, and Time-Restricted Feeding in Healthy Lifespan.Cell Metab. 2016 Jun 14;23(6):1048-1059. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.06.001. Cell Metab. 2016. PMID: 27304506 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Obesity, Senescence, and Senolytics.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022;274:165-180. doi: 10.1007/164_2021_555. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34697668
-
Complex physiology and clinical implications of time-restricted eating.Physiol Rev. 2022 Oct 1;102(4):1991-2034. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00006.2022. Epub 2022 Jul 14. Physiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35834774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of exercise on cellular and tissue aging.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 May 13;13(10):14522-14543. doi: 10.18632/aging.203051. Epub 2021 May 13. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34001677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin and tBHQ Treatment Combined with an Exercise Regime Prevents Osteosarcopenic Obesity in Middle-Aged Wistar Female Rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Aug 14;2021:5294266. doi: 10.1155/2021/5294266. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34447486 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture versus sham acupuncture for simple obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Postgrad Med J. 2020 Apr;96(1134):221-227. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2019-137221. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Postgrad Med J. 2020. PMID: 32015189 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlers, I. , Smajda, B. , & Ahlersova, E. (1980). Circadian rhythm of plasma and adrenal corticosterone in rats: Effect of restricted feeding schedules. Endocrinologia Experimentalis, 14(3), 183–190. - PubMed
-
- Bernardo, B. L. , Wachtmann, T. S. , Cosgrove, P. G. , Kuhn, M. , Opsahl, A. C. , Judkins, K. M. , … LeBrasseur, N. K. (2010). Postnatal PPARdelta activation and myostatin inhibition exert distinct yet complimentary effects on the metabolic profile of obese insulin‐resistant mice. PLoS ONE, 5(6), e11307 10.1371/journal.pone.0011307 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

