Outcomes in Patients Treated With Thin-Strut, Very Thin-Strut, or Ultrathin-Strut Drug-Eluting Stents in Small Coronary Vessels: A Prespecified Analysis of the Randomized BIO-RESORT Trial
- PMID: 31111862
- PMCID: PMC6537851
- DOI: 10.1001/jamacardio.2019.1776
Outcomes in Patients Treated With Thin-Strut, Very Thin-Strut, or Ultrathin-Strut Drug-Eluting Stents in Small Coronary Vessels: A Prespecified Analysis of the Randomized BIO-RESORT Trial
Abstract
Importance: Stenting small-vessel lesions has an increased adverse cardiovascular event risk. Very thin-strut or ultrathin-strut drug-eluting stents might reduce this risk, but data are scarce.
Objective: To assess the outcome of all-comer patients with small coronary vessel lesions treated with 3 dissimilar types of drug-eluting stents.
Design: This is a prespecified substudy of the Comparison of Biodegradable Polymer and Durable Polymer Drug-eluting Stents in an All Comers Population (BIO-RESORT) trial, an investigator-initiated, randomized, patient-blinded comparative clinical drug-eluting stent trial. Patients treated with ultrathin-strut sirolimus-eluting stents, very thin-strut everolimus-eluting stents, or previous-generation thin-strut zotarolimus-eluting stents were enrolled from December 2012 to August 2015. This multicenter trial was conducted in 4 Dutch centers for cardiac intervention. Of all 3514 all-comer BIO-RESORT participants, 1506 patients with treatment in at least 1 small-vessel lesion (reference vessel <2.5 mm) were included. Data were analyzed between September 2018 and February 2019.
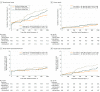
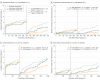
Main outcomes and measures: Target lesion failure at 3-year follow-up, a composite of cardiac death, target vessel-related myocardial infarction, or target lesion revascularization, analyzed by Kaplan-Meier methods.
Results: In 1452 of 1506 participants (96.4%) (1057 men [70.2%]; 449 women [29.8%]; mean [SD] age, 64.3 [10.4] years), follow-up was available. Target lesion failure occurred in 36 of 525 patients (7.0%) treated with sirolimus-eluting stents, 46 of 496 (9.5%) with everolimus-eluting stents, and 48 of 485 (10.0%) with zotarolimus-eluting stents (sirolimus-eluting vs zotarolimus-eluting hazard ratio [HR], 0.68; 95% CI, 0.44-1.05; P = .08; everolimus-eluting vs zotarolimus-eluting HR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.62-1.39; P = .72). There was a difference in target lesion revascularizations between sirolimus-eluting and zotarolimus-eluting stents (2.1% vs 5.3%; HR, 0.40; 95% CI, 0.20-0.81; P = .009) that emerged after the first year of follow-up (1.0% vs 3.7%; P = .006); multivariate analysis showed that sirolimus-eluting stent implantation was independently associated with a lower target lesion revascularization rate at 3-year follow-up (adjusted HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.20-0.85; P = .02). In the everolimus-eluting stents, the revascularization rate was 4.0% (vs zotarolimus-eluting, HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.41-1.34; P = .31). There was no significant between-stent difference in cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction, or stent thrombosis.
Conclusions and relevance: Patients stented in small coronary vessels experienced fewer repeated revascularizations if treated with ultrathin-strut sirolimus-eluting stents vs previous generation thin strut zotarolimus-eluting stents. Further research is required to evaluate the potential effect of particularly thin stent struts.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01674803.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
When Can Strut Thickness Really Matter in Percutaneous Coronary Intervention?JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Jul 1;4(7):669-670. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2019.1902. JAMA Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31111869 No abstract available.
-
Ultrathin Strut Stents in Small Coronary Vessels-Are We There Yet?JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Dec 1;4(12):1299. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2019.3906. JAMA Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31617860 No abstract available.
-
Ultrathin Strut Stents in Small Coronary Vessels-Are We There Yet?-Reply.JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Dec 1;4(12):1299-1300. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2019.3915. JAMA Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31617861 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wykrzykowska JJ, Serruys PW, Onuma Y, et al. Impact of vessel size on angiographic and clinical outcomes of revascularization with biolimus-eluting stent with biodegradable polymer and sirolimus-eluting stent with durable polymer the LEADERS trial substudy. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2009;2(9):861-870. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2009.05.024 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Claessen BE, Smits PC, Kereiakes DJ, et al. Impact of lesion length and vessel size on clinical outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention with everolimus- versus paclitaxel-eluting stents pooled analysis from the SPIRIT (Clinical Evaluation of the XIENCE V Everolimus Eluting Coronary Stent System) and COMPARE (second-generation everolimus-eluting and paclitaxel-eluting stents in real-life practice) Randomized Trials. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;4(11):1209-1215. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2011.07.016 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

