Functional and anatomical specificity in a higher olfactory centre
- PMID: 31112127
- PMCID: PMC6550879
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.44590
Functional and anatomical specificity in a higher olfactory centre
Abstract
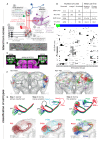
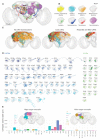
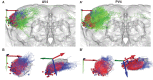
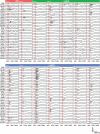
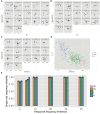
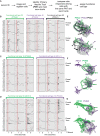
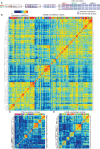
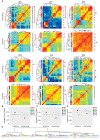
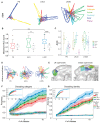
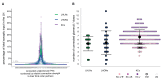
Most sensory systems are organized into parallel neuronal pathways that process distinct aspects of incoming stimuli. In the insect olfactory system, second order projection neurons target both the mushroom body, required for learning, and the lateral horn (LH), proposed to mediate innate olfactory behavior. Mushroom body neurons form a sparse olfactory population code, which is not stereotyped across animals. In contrast, odor coding in the LH remains poorly understood. We combine genetic driver lines, anatomical and functional criteria to show that the Drosophila LH has ~1400 neurons and >165 cell types. Genetically labeled LHNs have stereotyped odor responses across animals and on average respond to three times more odors than single projection neurons. LHNs are better odor categorizers than projection neurons, likely due to stereotyped pooling of related inputs. Our results reveal some of the principles by which a higher processing area can extract innate behavioral significance from sensory stimuli.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; Drosophila; cell type; lateral Horn; neuroanatomy; neuroscience; olfaction.
© 2019, Frechter et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SF, AB, ST, MD, JM, AJ, JK, DB, GJ No competing interests declared
Figures





References
-
- Aso Y, Sitaraman D, Ichinose T, Kaun KR, Vogt K, Belliart-Guérin G, Plaçais PY, Robie AA, Yamagata N, Schnaitmann C, Rowell WJ, Johnston RM, Ngo TT, Chen N, Korff W, Nitabach MN, Heberlein U, Preat T, Branson KM, Tanimoto H, Rubin GM. Mushroom body output neurons encode Valence and guide memory-based action selection in Drosophila. eLife. 2014b;3:e04580. doi: 10.7554/eLife.04580. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

