Traditional and Novel Mechanisms of Heat Shock Protein 90 (HSP90) Inhibition in Cancer Chemotherapy Including HSP90 Cleavage
- PMID: 31113013
- PMCID: PMC6720532
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2019.051
Traditional and Novel Mechanisms of Heat Shock Protein 90 (HSP90) Inhibition in Cancer Chemotherapy Including HSP90 Cleavage
Abstract
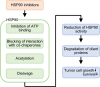
HSP90 is a molecular chaperone that increases the stability of client proteins. Cancer cells show higher HSP90 expression than normal cells because many client proteins play an important role in the growth and survival of cancer cells. HSP90 inhibitors mainly bind to the ATP binding site of HSP90 and inhibit HSP90 activity, and these inhibitors can be distinguished as ansamycin and non-ansamycin depending on the structure. In addition, the histone deacetylase inhibitors inhibit the activity of HSP90 through acetylation of HSP90. These HSP90 inhibitors have undergone or are undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of cancer. On the other hand, recent studies have reported that various reagents induce cleavage of HSP90, resulting in reduced HSP90 client proteins and growth suppression in cancer cells. Cleavage of HSP90 can be divided into enzymatic cleavage and non-enzymatic cleavage. Therefore, reagents inducing cleavage of HSP90 can be classified as another class of HSP90 inhibitors. We discuss that the cleavage of HSP90 can be another mechanism in the cancer treatment by HSP90 inhibition.
Keywords: ATP binding; Acetylation; Anti-cancer therapy; HSP90 cleavage; HSP90 inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: a novel basis for antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul 22;280(29):26729-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C500186200. Epub 2005 Jun 2. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15937340
-
HDAC6 inhibition enhances 17-AAG--mediated abrogation of hsp90 chaperone function in human leukemia cells.Blood. 2008 Sep 1;112(5):1886-93. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-03-143644. Epub 2008 Jun 30. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18591380
-
Hydroxamic acid analogue histone deacetylase inhibitors attenuate estrogen receptor-alpha levels and transcriptional activity: a result of hyperacetylation and inhibition of chaperone function of heat shock protein 90.Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Aug 15;13(16):4882-90. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-3093. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17699868
-
Anticancer Inhibitors of Hsp90 Function: Beyond the Usual Suspects.Adv Cancer Res. 2016;129:51-88. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2015.12.001. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Adv Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26916001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Posttranslational modification and beyond: interplay between histone deacetylase 6 and heat-shock protein 90.Mol Med. 2021 Sep 16;27(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00375-3. Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34530730 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cleavage of HSP90β induced by histone deacetylase inhibitor and proteasome inhibitor modulates cell growth and apoptosis.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2021 Jan;26(1):129-139. doi: 10.1007/s12192-020-01161-6. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2021. PMID: 32869129 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted delivery of heat shock protein 90 inhibitors prevents growth of HER2-positive tumor.Biomaterials. 2021 Jun;273:120817. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.120817. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Biomaterials. 2021. PMID: 33894402 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of HSP90 Cleavage to the Cytotoxic Effect of Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid In Vivo and the Involvement of TXNIP in HSP90 Cleavage.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2024 Jan 1;32(1):115-122. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2023.104. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2024. PMID: 38148557 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of protein domain mutations in cancer therapy.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 9;10(6):e27655. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27655. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38509890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using ChEMBL to Complement Schistosome Drug Discovery.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 28;15(5):1359. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051359. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242601 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bali P, Pranpat M, Bradner J, Balasis M, Fiskus W, Guo F, Rocha K, Kumaraswamy S, Boyapalle S, Atadja P, Seto E, Bhalla K. Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: a novel basis for antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 2005a;280:26729–26734. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C500186200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Banerji U, O’Donnell A, Scurr M, Pacey S, Stapleton S, Asad Y, Simmons L, Maloney A, Raynaud F, Campbell M, Walton M, Lakhani S, Kaye S, Workman P, Judson I. Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of 17-allylamino, 17-demethoxygeldanamycin in patients with advanced malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2005a;23:4152–4161. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.00.612. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

