Development of human cGAS-specific small-molecule inhibitors for repression of dsDNA-triggered interferon expression
- PMID: 31113940
- PMCID: PMC6529454
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-08620-4
Development of human cGAS-specific small-molecule inhibitors for repression of dsDNA-triggered interferon expression
Abstract
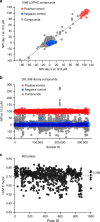
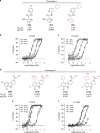
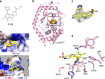
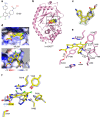
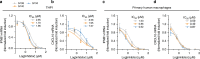
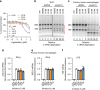
Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) is the primary sensor for aberrant intracellular dsDNA producing the cyclic dinucleotide cGAMP, a second messenger initiating cytokine production in subsets of myeloid lineage cell types. Therefore, inhibition of the enzyme cGAS may act anti-inflammatory. Here we report the discovery of human-cGAS-specific small-molecule inhibitors by high-throughput screening and the targeted medicinal chemistry optimization for two molecular scaffolds. Lead compounds from one scaffold co-crystallize with human cGAS and occupy the ATP- and GTP-binding active site. The specificity and potency of these drug candidates is further documented in human myeloid cells including primary macrophages. These novel cGAS inhibitors with cell-based activity will serve as probes into cGAS-dependent innate immune pathways and warrant future pharmacological studies for treatment of cGAS-dependent inflammatory diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
T.T., L.L., D.J.P., J.F.G., D.T., T.Ka., Mi.M., Y.A., R.O., S.H., J.A., T.I., Ma.M. and T.Ku. have filed a patent application encompassing aspects of this work (PCT/US2019/016673). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

