Epigenetic dysregulation of enhancers in neurons is associated with Alzheimer's disease pathology and cognitive symptoms
- PMID: 31113950
- PMCID: PMC6529540
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-10101-7
Epigenetic dysregulation of enhancers in neurons is associated with Alzheimer's disease pathology and cognitive symptoms
Abstract
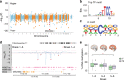
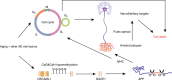
Epigenetic control of enhancers alters neuronal functions and may be involved in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Here, we identify enhancers in neurons contributing to AD by comprehensive fine-mapping of DNA methylation at enhancers, genome-wide. We examine 1.2 million CpG and CpH sites in enhancers in prefrontal cortex neurons of individuals with no/mild, moderate, and severe AD pathology (n = 101). We identify 1224 differentially methylated enhancer regions; most of which are hypomethylated at CpH sites in AD neurons. CpH methylation losses occur in normal aging neurons, but are accelerated in AD. Integration of epigenetic and transcriptomic data demonstrates a pro-apoptotic reactivation of the cell cycle in post-mitotic AD neurons. Furthermore, AD neurons have a large cluster of significantly hypomethylated enhancers in the DSCAML1 gene that targets BACE1. Hypomethylation of these enhancers in AD is associated with an upregulation of BACE1 transcripts and an increase in amyloid plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, and cognitive decline.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Dementia. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs362/en/ (2017).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 15110/Scottish Rite Charitable Foundation of Canada (SRCFC)/International
- R01 AG030146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- PD170089/U.S. Department of Defense (United States Department of Defense)/International
- R01 ES024992/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R25 DA027995/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 ES026699/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG036042/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG009391/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH088413/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046152/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG007175/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG036042/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA200060/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG007354/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG036836/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

