Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic study of posaconazole delayed-release tablet in a patient with coexisting invasive aspergillosis and mucormycosis
- PMID: 31114213
- PMCID: PMC6497849
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S203625
Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic study of posaconazole delayed-release tablet in a patient with coexisting invasive aspergillosis and mucormycosis
Abstract
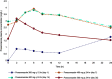
Limited information exists regarding the optimal dose of posaconazole delayed-release tablet for the treatment of invasive mold infection. Here, we report the case of a previously healthy 44-year-old Thai man who developed coexisting invasive pulmonary aspergillosis and mucormycosis following a car accident. He was treated with posaconazole delayed-release tablet. This report describes the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic study, safety profile, and determination of the appropriate dosage of posaconazole delayed-release tablet in a patient with coexisting invasive aspergillosis and mucormycosis. Posaconazole exposure was analyzed by noncompartmental model. Ratio of area under the plasma concentration-time curve over the minimum inhibitory concentration (AUC/MIC) was applied to maximize the efficacy of posaconazole. The loading dose of 300 mg q 12 hrs was found to be potentially insufficient for achieving the AUC/MIC target for treatment of invasive mold infection with minimum inhibitory concentrations >0.01 mg/L. Early therapeutic drug monitoring to detect the drug concentration of posaconazole delayed-release tablet is necessary so that dosing adjustments can be made, as needed. In addition, a maintenance dose of either 400 or 300 mg once daily could achieve the AUC/MIC targets. These maintenance dosing regimens effectuated a successful clinical outcome with minimal adverse events.
Keywords: AUC/MIC; antifungal; invasive fungal infection; mixed infection; therapeutic drug monitoring; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no personal or professional conflicts of interest, and no financial support from the companies that produce and/or distribute the drugs, devices, or materials described in this report.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluating posaconazole dosing regimens of the different formulations against Aspergillus spp. in adults: a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analysis using Monte Carlo simulation.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Oct;56(4):106112. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106112. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020. PMID: 32721598
-
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of posaconazole for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: clinical implications for antifungal therapy.J Infect Dis. 2011 May 1;203(9):1324-32. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir023. Epub 2011 Feb 28. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21357943 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics and safety of posaconazole delayed-release tablets for invasive fungal infections.Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Dec 23;8:1-8. doi: 10.2147/CPAA.S60933. eCollection 2016. Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26730212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevention of Invasive Aspergillus Fungal Infections with the Suspension and Delayed-Release Tablet Formulations of Posaconazole in Patients with Haematologic Malignancies.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 26;8(1):1681. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20136-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29374234 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Posaconazole: an Update.Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2016;10:51-61. doi: 10.1007/s12281-016-0255-4. Epub 2016 May 7. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2016. PMID: 27358662 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
COVID-19-associated mixed mold infection: A case report of aspergillosis and mucormycosis and a literature review.J Mycol Med. 2022 Mar;32(1):101231. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2021.101231. Epub 2021 Nov 26. J Mycol Med. 2022. PMID: 34864498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extrapolating Antifungal Animal Data to Humans - Is it reliable?Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2020 Mar;14(1):50-62. doi: 10.1007/s12281-020-00370-x. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2020. PMID: 32201545 Free PMC article.
-
The Clinically Approved Antifungal Drug Posaconazole Inhibits Human Cytomegalovirus Replication.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Sep 21;64(10):e00056-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00056-20. Print 2020 Sep 21. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32690644 Free PMC article.
-
Successful treatment of mixed pulmonary Aspergillus and Mucor infection using intrabronchial amphotericin B infusion: a case report and literature review.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Sep 4;24(1):436. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03234-z. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 39232717 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

