Neuroprotective Effect of Cardamom Oil Against Aluminum Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats
- PMID: 31114535
- PMCID: PMC6502995
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00399
Neuroprotective Effect of Cardamom Oil Against Aluminum Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats
Abstract
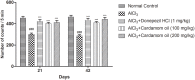
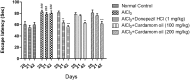
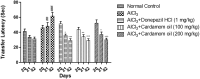
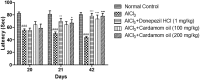
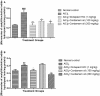
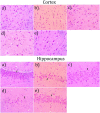
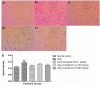
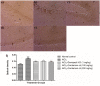
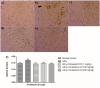
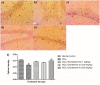
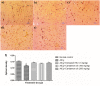
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is an enzyme involved in the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Cardamom oil (CO) has been reported to have acetylcholinesterase inhibitory, antioxidant and anti-anxiety effects. Hence, we studied the effect of cardamom oil in aluminum chloride induced neurotoxicity in rats. AD like symptoms were induced in Wistar rats with aluminum chloride (100 mg/kg, p.o.). Cardamom oil was administered concomitantly by oral route at doses of 100 and 200 mg/kg for 42 days. Behavioral parameters like Morris water maze, elevated plus maze, passive avoidance test and locomotor activity were evaluated on day 21 and 42. AChE activity, oxidative stress parameters, histopathological studies and immunohistochemistry studies were carried out in hippocampus and cortex. Cardamom oil treatment showed significant improvement in behavioral parameters, inhibition of AChE activity (p < 0.001) and reduction in oxidative stress in the brain. Histopathological studies of hippocampus and cortex by hematoxylin & eosin (H. & E.) and congo red stain showed inhibition of neuronal damage and amyloid β plaque formation with cardamom oil treatment. Immunohistochemistry showed, CO treatment inhibited amyloid β expression and upregulated brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). The present study showed that, cardamom oil has neuroprotective effect in aluminum chloride induced neurotoxicity linked with inhibition of AChE activity and reduction in oxidative damage. This effect of cardamom oil may be useful in management of Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; acetylcholinesterase; aluminum; cardamom oil; neuroprotective; oxidative stress.
Figures

References
-
- Ko Y-H, Kwon S-H, Ma S-X, Seo J-Y, Lee B-R, Kim K, et al. . The memory-enhancing effects of 7,8,4'-trihydroxyisoflavone, a major metabolite of daidzein, are associated with activation of the cholinergic system and BDNF signaling pathway in mice. Brain Res Bull. (2018) 142:197–206. 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.07.012 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kaizer RR, Corrêa MC, Spanevello RM, Morsch VM, Mazzanti CM, Gonçalves JF, et al. . Acetylcholinesterase activation and enhanced lipid peroxidation after long-term exposure to low levels of aluminum on different mouse brain regions. J Inorg Biochem. (2005) 99:1865–70. 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2005.06.015 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

