Roles of Type 1 Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Receptor and IGF-II in Growth Regulation: Evidence From a Patient Carrying Both an 11p Paternal Duplication and 15q Deletion
- PMID: 31114545
- PMCID: PMC6503735
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00263
Roles of Type 1 Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Receptor and IGF-II in Growth Regulation: Evidence From a Patient Carrying Both an 11p Paternal Duplication and 15q Deletion
Abstract
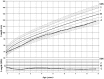
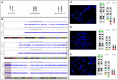
We report an original association of complex genetic defects in a patient carrying both an 11p paternal duplication, resulting in the double expression of insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2), as reported in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, and a 15q terminal deletion, including the type 1 IGF receptor gene (IGF1R), resulting in haploinsufficiency for this gene. The patient was born with measurements appropriate for her gestational age but experienced growth retardation in early childhood, allowing a better comprehension of the IGF system in the pathophysiology of growth. It is possible that IGF-II plays a key role in fetal growth, independently of IGF1R signaling, and that its role is less important in post-natal growth, leaving IGF-I and growth hormone as the main actors.
Keywords: 11p duplication; Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome; IGF-II; IGF1 receptor; fetal growth restriction; imprinting disease.
Figures

References
-
- LeRoith D, Werner H, Beitner-Johnson D, Roberts CT. Molecular and cellular aspects of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Endocr Rev. (1995) 16:143–63. - PubMed
-
- Brioude F, Kalish JM, Mussa A, Foster AC, Bliek J, Ferrero GB, et al. . Expert consensus document: clinical and molecular diagnosis, screening and management of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: an international consensus statement. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2018) 14:229–49. 10.1038/nrendo.2017.166 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

