Hepatic Natural Killer Cells: Organ-Specific Sentinels of Liver Immune Homeostasis and Physiopathology
- PMID: 31114585
- PMCID: PMC6502999
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00946
Hepatic Natural Killer Cells: Organ-Specific Sentinels of Liver Immune Homeostasis and Physiopathology
Abstract
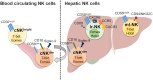
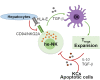
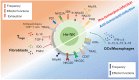
The liver is considered a preferential tissue for NK cells residency. In humans, almost 50% of all intrahepatic lymphocytes are NK cells that are strongly imprinted in a liver-specific manner and show a broad spectrum of cellular heterogeneity. Hepatic NK (he-NK) cells play key roles in tuning liver immune response in both physiological and pathological conditions. Therefore, there is a pressing need to comprehensively characterize human he-NK cells to better understand the related mechanisms regulating their effector-functions within the dynamic balance between immune-tolerance and immune-surveillance. This is of particular relevance in the liver that is the only solid organ whose parenchyma is constantly challenged on daily basis by millions of foreign antigens drained from the gut. Therefore, the present review summarizes our current knowledge on he-NK cells in the light of the latest discoveries in the field of NK cell biology and clinical relevance.
Keywords: Natural Kill cell; homeostais; homeostasis; liver; tissue immunity.
Figures