FLASH: a next-generation CRISPR diagnostic for multiplexed detection of antimicrobial resistance sequences
- PMID: 31114866
- PMCID: PMC6698650
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkz418
FLASH: a next-generation CRISPR diagnostic for multiplexed detection of antimicrobial resistance sequences
Abstract
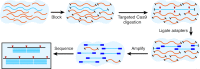
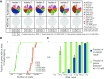
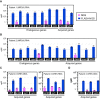
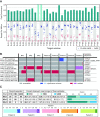
The growing prevalence of deadly microbes with resistance to previously life-saving drug therapies is a dire threat to human health. Detection of low abundance pathogen sequences remains a challenge for metagenomic Next Generation Sequencing (NGS). We introduce FLASH (Finding Low Abundance Sequences by Hybridization), a next-generation CRISPR/Cas9 diagnostic method that takes advantage of the efficiency, specificity and flexibility of Cas9 to enrich for a programmed set of sequences. FLASH-NGS achieves up to 5 orders of magnitude of enrichment and sub-attomolar gene detection with minimal background. We provide an open-source software tool (FLASHit) for guide RNA design. Here we applied it to detection of antimicrobial resistance genes in respiratory fluid and dried blood spots, but FLASH-NGS is applicable to all areas that rely on multiplex PCR.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- O’Neill J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance. 2016.
-
- Zaas A.K., Garner B.H., Tsalik E.L., Burke T., Woods C.W., Ginsburg G.S.. The current epidemiology and clinical decisions surrounding acute respiratory infections. Trends Mol. Med. 2014; 20:579–588. - PubMed
-
- van der Eerden M.M., Vlaspolder F., de Graaff C.S., Groot T., Bronsveld W., Jansen H.M., Boersma W.G.. Comparison between pathogen directed antibiotic treatment and empirical broad spectrum antibiotic treatment in patients with community acquired pneumonia: a prospective randomised study. Thorax. 2005; 60:672–678. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

