Delivery of natural phenolic compounds for the potential treatment of lung cancer
- PMID: 31115871
- PMCID: PMC6593021
- DOI: 10.1007/s40199-019-00267-2
Delivery of natural phenolic compounds for the potential treatment of lung cancer
Abstract
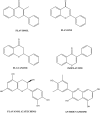
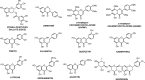
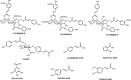
The application of natural products to treat various diseases, such as cancer, has been an important area of research for many years. Several phytochemicals have demonstrated anticarcinogenic activity to prevent or reduce the progression of cancer by modulating various cellular mechanisms. However, poor bioavailability has hindered clinical success and the incorporation of these drugs into efficient drug delivery systems would be beneficial. For lung cancer, local delivery via the pulmonary route would also be more effective. In this article, recent in vitro scientific literature on phenolic compounds with anticancer activity towards lung cancer cell lines is reviewed and nanoparticulate delivery is mentioned as a possible solution to the problem of bioavailability. The first part of the review will explore the different classes of natural phenolic compounds and discuss recent reports on their activity on lung cancer cells. Then, the problem of the poor bioavailability of phenolic compounds will be explored, followed by a summary of recent advances in improving the efficacy of these phenolic compounds using nanoparticulate drug delivery systems. Graphical abstract The rationale for direct delivery of phenolic compounds loaded in microparticles to the lungs.
Keywords: Drug delivery; Lung cancer; Phenolic compound; Polymeric nanoparticle; Pulmonary delivery.
Figures



References
-
- Cancer Research UK. Lung cancer statistics.2018. https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/s.... Accessed 13 Jul 2018.
-
- Heleno SA, Martins A, Queiroz MJRP, Ferreira ICFR. Bioactivity of phenolic acids: metabolites versus parent compounds: a review. Food Chem. 2015;173:501–513. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

