Bone marrow stromal cells interaction with titanium; Effects of composition and surface modification
- PMID: 31116747
- PMCID: PMC6530826
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216087
Bone marrow stromal cells interaction with titanium; Effects of composition and surface modification
Abstract
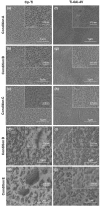
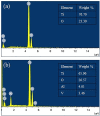
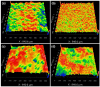
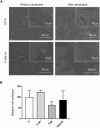
Inflammation and implant loosening are major concerns when using titanium implants for hard tissue engineering applications. Surface modification is one of the promising tools to enhance tissue-material integration in metallic implants. Here, we used anodization technique to modify the surface of commercially pure titanium (CP-Ti) and titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) samples. Our results show that electrolyte composition, anodization time and voltage dictated the formation of well-organized nanotubes. Although electrolyte containing HF in water resulted in nanotube formation on Ti, the presence of NH4F and ethylene glycol was necessary for successful nanotube formation on Ti-6Al-4V. Upon examination of the interaction of bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) with the modified samples, we found that Ti-6Al-4V without nanotubes induced cell proliferation and cluster of differentiation 40 ligand (CD40L) expression which facilitates B-cell activation to promote early bone healing. However, the expression of glioma associated protein 2 (GLI2), which regulates CD40L, was reduced in Ti-6Al-4V and the presence of nanotubes further reduced its expression. The inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) expression was reduced by nanotube presence on Ti. These results suggest that Ti-6Al-4V with nanotubes may be suitable implants because they have no effect on BMSC growth and inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Schiff N, Grosgogeat B, Lissac M, Dalard F. Influence of fluoride content and pH on the corrosion resistance of titanium and its alloys. Biomaterials. 2002;23: 1995–2002. - PubMed
-
- Geetha M, Singh AK, Asokamani R, Gogia AK. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants–A review. Prog Mater Sci. 2009;54: 397–425. 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2008.06.004 - DOI
-
- Bortolan C, Campanelli L, Bolfarini C, Oliveira N. Fatigue strength of Ti-6A1-4V alloy with surface modified by TiO2 nanotubes formation. Mater Lett. 2016;177: 46–49. 10.1016/j.matlet.2016.04.188 - DOI
-
- Liu X, Chu PK, Ding C. Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng R Rep. 2004;47: 49–121. 10.1016/j.mser.2004.11.001 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

