AKI Associated with Acute Pancreatitis
- PMID: 31118209
- PMCID: PMC6625613
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.13191118
AKI Associated with Acute Pancreatitis
Abstract
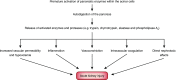
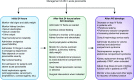
Acute pancreatitis is a common disorder of the pancreas. It is the most frequent gastrointestinal cause for hospitalization and one of the leading causes of in-hospital deaths. Its severity ranges from mild self-limited disease to severe acute necrotizing pancreatitis characterized by systemic complications and multiorgan failure. Severe acute pancreatitis develops in about 20% of patients with acute pancreatitis and may be associated with multiorgan failure (respiratory, cardiovascular, and kidney). AKI is a frequent complication of severe acute pancreatitis and develops late in the course of the disease, usually after the failure of other organs. It carries a very poor prognosis, particularly if kidney replacement therapy is required, with mortality rates exceeding 75%. The exact pathophysiology of AKI in acute pancreatitis remains unclear but appears to result from initial volume depletion followed by complex vascular and humoral factors. Here, we provide an overview of the epidemiology, pathogenesis, causes, and management of AKI in patients with severe acute pancreatitis.
Keywords: Abdominal Compartment Syndrome; Acute Kidney Injury; Acute Pancreatitis; Hospital Mortality; Hypovolemia; Kidney Replacement Therapy; Multiple Organ Failure; Pancreatitis, Acute Necrotizing; Prognosis; Renal Replacement Therapy; hospitalization; kidney.
Copyright © 2019 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, Tsiotos GG, Vege SS; Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working Group: Classification of acute pancreatitis--2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 62: 102–111, 2013 - PubMed
-
- Tenner S, Baillie J, DeWitt J, Vege SS, American College of Gastroenterology. American college of gastroenterology guideline: Management of acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 108: 1400–1415; 1416, 2013 - PubMed
-
- Devani K, Charilaou P, Radadiya D, Brahmbhatt B, Young M, Reddy C: Acute pancreatitis: Trends in outcomes and the role of acute kidney injury in mortality- A propensity-matched analysis. Pancreatology 18: 870–877, 2018 - PubMed
-
- Tran DD, Oe PL, de Fijter CW, van der Meulen J, Cuesta MA: Acute renal failure in patients with acute pancreatitis: Prevalence, risk factors, and outcome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 8: 1079–1084, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Kes P, Vucicević Z, Ratković-Gusić I, Fotivec A: Acute renal failure complicating severe acute pancreatitis. Ren Fail 18: 621–628, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

