Randomized phase 2 study of FcRn antagonist efgartigimod in generalized myasthenia gravis
- PMID: 31118245
- PMCID: PMC6556100
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007600
Randomized phase 2 study of FcRn antagonist efgartigimod in generalized myasthenia gravis
Erratum in
-
Randomized Phase 2 Study of FcRn Antagonist Efgartigimod in Generalized Myasthenia Gravis.Neurology. 2025 Feb 11;104(3):e210299. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000210299. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Neurology. 2025. PMID: 39813633 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: To investigate safety and explore efficacy of efgartigimod (ARGX-113), an anti-neonatal Fc receptor immunoglobulin G1 Fc fragment, in patients with generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) with a history of anti-acetylcholine receptor (AChR) autoantibodies, who were on stable standard-of-care myasthenia gravis (MG) treatment.
Methods: A phase 2, exploratory, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 15-center study is described. Eligible patients were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive 4 doses over a 3-week period of either 10 mg/kg IV efgartigimod or matched placebo combined with their standard-of-care therapy. Primary endpoints were safety and tolerability. Secondary endpoints included efficacy (change from baseline to week 11 of Myasthenia Gravis Activities of Daily Living, Quantitative Myasthenia Gravis, and Myasthenia Gravis Composite disease severity scores, and of the revised 15-item Myasthenia Gravis Quality of Life scale), pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunogenicity.
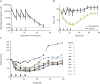
Results: Of the 35 screened patients, 24 were enrolled and randomized: 12 received efgartigimod and 12 placebo. Efgartigimod was well-tolerated in all patients, with no serious or severe adverse events reported, no relevant changes in vital signs or ECG findings observed, and no difference in adverse events between efgartigimod and placebo treatment. All patients treated with efgartigimod showed a rapid decrease in total immunoglobulin G (IgG) and anti-AChR autoantibody levels, and assessment using all 4 efficacy scales consistently demonstrated that 75% showed a rapid and long-lasting disease improvement.
Conclusions: Efgartigimod was safe and well-tolerated. The correlation between reduction of levels of pathogenic IgG autoantibodies and disease improvement suggests that reducing pathogenic autoantibodies with efgartigimod may offer an innovative approach to treat MG.
Classification of evidence: This study provides Class I evidence that efgartigimod is safe and well-tolerated in patients with gMG.
© 2019 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures



Comment in
-
Efgartigimod: A novel antibody depletion therapy in myasthenia gravis.Neurology. 2019 Jun 4;92(23):1079-1080. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007605. Epub 2019 May 22. Neurology. 2019. PMID: 31118243 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gilhus NE. Myasthenia gravis. N Engl J Med 2016;375:2570–2581. - PubMed
-
- Gilhus NE, Verschuuren JJ. Myasthenia gravis: subgroup classification and therapeutic strategies. Lancet Neurol 2015;14:1023–1036. - PubMed
-
- Roopenian DC, Akilesh S. FcRn: the neonatal Fc receptor comes of age. Nat Rev Immunol 2007;7:715–725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
