Prognostic value of the association between MHC class I downregulation and PD-L1 upregulation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients
- PMID: 31118488
- PMCID: PMC6531443
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-44206-2
Prognostic value of the association between MHC class I downregulation and PD-L1 upregulation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients
Abstract
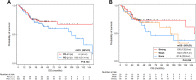
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the prognostic impact of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I expression and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). A total of 158 patients with HNSCC were evaluated retrospectively. The expression of MHC class I and PD-L1 was analyzed in tumor specimens using immunohistochemistry. The association between MHC class I/PD-L1 expression and clinical outcome was evaluated by Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression analyses. Among 158 patients, 103 (65.2%) showed positive PD-L1 expression, and 20 (12.7%) showed no detectable expression of MHC class I. The frequency of PD-L1 positive expression with concomitant MHC class I loss was 7.0%. In the PD-L1-positive group, MHC class I loss was associated with a significantly worse survival compared with MHC class I positivity (median overall survival 39.3 months vs. not reached; P = 0.005), whereas MHC class I status provided no prognostic impact in the PD-L1 negative group. Neither PD-L1 nor MHC class I alone showed a significant difference in overall survival. The loss of MHC class I expression in PD-L1-positive HNSCC was associated with a poor clinical outcome. This suggested that MHC class I expression status might be useful for the prognosis of tumor progression in HNSCC when combined with PD-L1 expression status. External validation with enough numbers of participants in such subgroup should be needed for validation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characteristics and impact of programmed death-ligand 1 expression, CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, and p16 status in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Med Oncol. 2019 Jan 21;36(2):21. doi: 10.1007/s12032-018-1241-1. Med Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30666437
-
Expression of PD-1/PD-L1 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and its clinical significance.Int J Biol Markers. 2019 Dec;34(4):398-405. doi: 10.1177/1724600819884722. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Int J Biol Markers. 2019. PMID: 31674884
-
PD-1 and PD-L1 expression in HNSCC primary cancer and related lymph node metastasis - impact on clinical outcome.Histopathology. 2018 Oct;73(4):573-584. doi: 10.1111/his.13646. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Histopathology. 2018. PMID: 29742291
-
The prognostic role of PD-L1 expression for survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Oral Oncol. 2018 Nov;86:81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2018.09.016. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Oral Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30409325
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of PD-L1 overexpression in oral squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and comprehensive meta-analysis.Oral Oncol. 2020 Jul;106:104722. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104722. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Oral Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32330687
Cited by
-
Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Gynecologic Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jul 28;15(15):3849. doi: 10.3390/cancers15153849. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting immune checkpoints in gynecologic cancer: updates & perspectives for pathologists.Mod Pathol. 2022 Feb;35(2):142-151. doi: 10.1038/s41379-021-00882-y. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Mod Pathol. 2022. PMID: 34493822 Review.
-
Resisting Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Therapy: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 27;21(17):6176. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176176. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32867025 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L1 Expression and a High Tumor Infiltrate of CD8+ Lymphocytes Predict Outcome in Patients with Oropharyngeal Squamous Cells Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 23;21(15):5228. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155228. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32718057 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 deserves attention in head and neck cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 2;13:988416. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.988416. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36119046 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

