Anti-neuroinflammatory effects of Ephedra sinica Stapf extract-capped gold nanoparticles in microglia
- PMID: 31118612
- PMCID: PMC6497913
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S195218
Anti-neuroinflammatory effects of Ephedra sinica Stapf extract-capped gold nanoparticles in microglia
Abstract
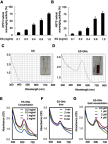
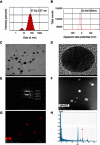
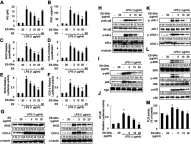
Background: Combination therapy remains a promising strategy for treating neurodegenerative diseases, although green synthesis of gold nanoparticles for treating chronic neuroinflammation and studying their efficacy in treating neuroinflammation-mediated neurodegenerative diseases is not well assessed. Results: Here, Ephedra sinica Stapf (ES) extract was used as the reducing, capping, and stabilizing agent for gold nanoparticle synthesis. We developed ES extract-capped gold nanoparticles (ES-GNs) and investigated their anti-neuroinflammatory properties in microglia. ES-GNs displayed maximum absorption at 538 nm in ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy. Dynamic light scattering assessment revealed that ES-GN diameter was 57.6±3.07 nm, with zeta potential value of -24.6±0.84 mV. High resolution-transmission electron microscopy confirmed the spherical shape and average diameter (35.04±4.02 nm) of ES-GNs. Crystalline structure of ES-GNs in optimal conditions was determined by X-ray powder diffraction, and elemental gold presence was confirmed by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy confirmed gold nanoparticle synthesis using ES. Anti-neuroinflammatory properties of ES-GNs on production of pro-inflammatory mediators (nitric oxide, prostaglandin E2, and reactive oxygen species) and cytokines (tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated microglia were investigated by ELISA and flow cytometry. ES-GNs significantly attenuated LPS-induced production of pro-inflammatory mediators and cytokines, which was related to suppressed transcription and translation of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2, determined by RT-PCR and western blotting. ES-GNs downregulated upstream signaling pathways (IκB kinase-α/β, nuclear factor-κB, Janus-activated kinase /signal transducers and activators of transcription, mitogen-activated protein kinase , and phospholipase D) of pro-inflammatory mediators and cytokines in LPS-stimulated microglia. Anti-neuroinflammatory properties of ES-GNs were mediated by ES-GNs-induced AMP-activated protein kinase)-mediated nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2 /antioxidant response element signaling. Conclusion: Collectively, these findings provide a new insight on the role of ES-GNs in treating chronic neuroinflammation-induced neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: Ephedra sinica Stapf; gold nanoparticle; microglia; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Kalopanacis Cortex extract-capped gold nanoparticles activate NRF2 signaling and ameliorate damage in human neuronal SH-SY5Y cells exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Jun 22;12:4563-4578. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S138178. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28790819 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effect of Dictyopteris divaricata extract-capped gold nanoparticles against oxygen and glucose deprivation/reoxygenation.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019 Jul 1;179:421-428. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.03.066. Epub 2019 Mar 29. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019. PMID: 31003168
-
Antimalarial Drug Artemether Inhibits Neuroinflammation in BV2 Microglia Through Nrf2-Dependent Mechanisms.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Nov;53(9):6426-6443. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9543-1. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26607631
-
The influence of polyphenol-rich extracts on the production of pro-inflammatory mediators in macrophages.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021 Apr;72(2). doi: 10.26402/jpp.2021.2.02. Epub 2021 Aug 6. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34374653 Review.
-
Intracellular signaling pathways modulated by phenolic compounds: application for new anti-inflammatory drugs discovery.Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(18):2876-900. doi: 10.2174/092986712800672049. Curr Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22519398 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticles and cytokine response.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Aug 28;11:1243651. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1243651. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37701495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gold Nanoparticles Using Ecklonia stolonifera Protect Human Dermal Fibroblasts from UVA-Induced Senescence through Inhibiting MMP-1 and MMP-3.Mar Drugs. 2020 Aug 19;18(9):433. doi: 10.3390/md18090433. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32825040 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Microglia in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Beneficial Effects of Docosahexahenoic Acid (DHA) Supplied by Food or Combined with Nanoparticles.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 30;22(19):10639. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910639. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional Nanocarriers for Alzheimer's Disease: Befriending the Barriers.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 May;61(5):3042-3089. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03730-z. Epub 2023 Nov 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37966683 Review.
-
Nanoparticles: A Hope for the Treatment of Inflammation in CNS.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 26;12:683935. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.683935. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34122112 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Singh P, Ahn S, Kang JP, et al. In vitro anti-inflammatory activity of spherical silver nanoparticles and monodisperse hexagonal gold nanoparticles by fruit extract of Prunus serrulata: a green synthetic approach. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(8):2022–2032. doi:10.1080/21691401.2017.1408117 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

