Mitochondrial Adaptations in Elderly and Young Men Skeletal Muscle Following 2 Weeks of Bed Rest and Rehabilitation
- PMID: 31118897
- PMCID: PMC6504794
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00474
Mitochondrial Adaptations in Elderly and Young Men Skeletal Muscle Following 2 Weeks of Bed Rest and Rehabilitation
Abstract
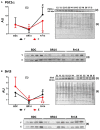
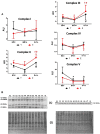
The aim of the study was to evaluate the expression levels of proteins related to mitochondrial biogenesis regulation and bioenergetics in vastus lateralis muscle biopsies from 16 elderly and 7 young people subjected to 14 days of bed-rest, causing atrophy, and subsequent 14 days of exercise training. Based on quantitative immunoblot analyses, in both groups a reduction of two key regulators of mitochondrial biogenesis/remodeling and activity, namely PGC-1α and Sirt3, was revealed during bed-rest, with a subsequent up-regulation after rehabilitation, indicating an involvement of PGC-1α-Sirt3 axis in response to the treatments. A difference was observed comparing the young and elderly subjects as, for both proteins, the abundance in the elderly was more affected by immobility and less responsive to exercise. The expression levels of TOM20 and Citrate Synthase, assayed as markers of outer mitochondrial membrane and mitochondrial mass, showed a noticeable sensitivity in the elderly group, where they were affected by bed-rest and rehabilitation recalling the pattern of PGC-1α. TOM20 and CS remained unchanged in young subjects. Single OXPHOS complexes showed peculiar patterns, which were in some cases dissimilar from PGC-1α, and suggest different influences on protein biogenesis and degradation. Overall, exercise was capable to counteract the effect of immobility, when present, except for complex V, which was markedly downregulated by bed-rest, but remained unaffected after rehabilitation, maybe as result of greater extent of degradation processes over biogenesis. Phosphorylation extent of AMPK, and its upstream activator LKB1, did not change after bed-rest and rehabilitation in either young or elderly subjects, suggesting that the activation of energy-sensing LKB1-AMPK signaling pathway was "missed" due to its transient nature, or was not triggered under our conditions. Our study demonstrates that, as far as the expression of various proteins related to mitochondrial biogenesis/remodeling, adaptations to bed-rest and rehabilitation in the two populations were different. The impact of bed-rest was greater in the elderly subjects, where the pattern (decrease after bed rest and recovery following rehabilitation) was accompanied by changes of mitochondrial mass. Modifications of protein abundance were matched with data obtained from gene expression analyses of four public human datasets focusing on related genes.
Keywords: aging; exercise; immobility; in silico gene expression data mining; mitochondria-related proteins; skeletal muscle; western blot.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate on skeletal muscle mitochondrial content and dynamics, and lipids after 10 days of bed rest in older adults.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017 Nov 1;123(5):1092-1100. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00192.2017. Epub 2017 Jul 13. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017. PMID: 28705993 Clinical Trial.
-
Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5507-9. doi: 10.2174/138161282035140911142118. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606795
-
Exercise training attenuates aging-associated mitochondrial dysfunction in rat skeletal muscle: role of PGC-1α.Exp Gerontol. 2013 Nov;48(11):1343-50. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2013.08.004. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Exp Gerontol. 2013. PMID: 23994518
-
Adaptation of Skeletal Muscles to Contractile Activity of Varying Duration and Intensity: The Role of PGC-1α.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2018 Jun;83(6):613-628. doi: 10.1134/S0006297918060019. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2018. PMID: 30195320 Review.
-
The impact of extended bed rest on the musculoskeletal system in the critical care environment.Extrem Physiol Med. 2015 Oct 9;4:16. doi: 10.1186/s13728-015-0036-7. eCollection 2015. Extrem Physiol Med. 2015. PMID: 26457181 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of bed rest on human skeletal muscle metabolism.Cell Rep Med. 2024 Jan 16;5(1):101372. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101372. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 38232697 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) Pathways in Age-Related Cardiovascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 29;9(11):1574. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111574. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Various Muscle Disuse States and Countermeasures on Muscle Molecular Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 31;23(1):468. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010468. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atenolol Ameliorates Skeletal Muscle Atrophy and Oxidative Stress Induced by Cast Immobilization in Rats.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 25;11(5):1269. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051269. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37238940 Free PMC article.
-
Menstrual cycle influence on skeletal muscle mitochondrial respiration in humans.Physiol Rep. 2025 Jul;13(13):e70458. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70458. Physiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40650425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alibegovic A. C., Hojbjerre L., Sonne M. P., Van Hall G., Alsted T. J., Kiens B., et al. (2010a). Increased rate of whole body lipolysis before and after 9 days of bed rest in healthy young men born with low birth weight. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 298 E555–E564. 10.1152/ajpendo.00223.2009 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alibegovic A. C., Sonne M. P., Højbjerre L., Bork-Jensen J., Jacobsen S., Nilsson E., et al. (2010b). Insulin resistance induced by physical inactivity is associated with multiple transcriptional changes in skeletal muscle in young men. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 299 E752–E763. 10.1152/ajpendo.00590.2009 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

