Sulodexide attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway
- PMID: 31120192
- PMCID: PMC6653332
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14367
Sulodexide attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway
Abstract
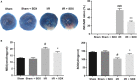
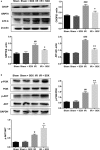
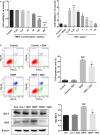
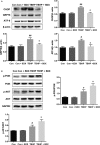
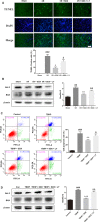
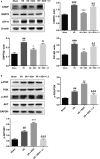
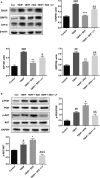
Acute myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion (MI/R) injury causes severe arrhythmias with a high rate of lethality. Extensive research focus on endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and its dysfunction which leads to cardiac injury in MI/R Our study evaluated the effects of sulodexide (SDX) on MI/R by establishing MI/R mice models and in vitro oxidative stress models in H9C2 cells. We found that SDX decreases cardiac injury during ischaemia reperfusion and decreased myocardial apoptosis and infarct area, which was paralleled by increased superoxide dismutase and reduced malondialdehyde in mice plasm, increased Bcl-2 expression, decreased BAX expression in a mouse model of MI/R. In vitro, SDX exerted a protective effect by the suppression of the ER stress which induced by tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) treatment. Both of the in vivo and in vitro effects were involved in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signalling pathway. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway by specific inhibitor, LY294002, partially reduced the protective effect of SDX. In short, our results suggested that the cardioprotective role of SDX was related to the suppression of ER stress in mice MI/R models and TBHP-induced H9C2 cell injury which was through the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway.
Keywords: PI3K/Akt; endoplasmic reticulum stress; myocardial ischaemia / reperfusion; sulodexide.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that the content of this article has no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Monassier JP. Reperfusion injury in acute myocardial infarction. From bench to cath lab. Part I: basic considerations. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2008;101:491‐500. - PubMed
-
- Penna C, Perrelli MG, Tullio F, et al. Diazoxide postconditioning induces mitochondrial protein S‐nitrosylation and a redox‐sensitive mitochondrial phosphorylation/translocation of RISK elements: no role for SAFE. Basic Res Cardiol. 2013;108:371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

