Expansion and Functional Divergence of Inositol Polyphosphate 5-Phosphatases in Angiosperms
- PMID: 31121965
- PMCID: PMC6562803
- DOI: 10.3390/genes10050393
Expansion and Functional Divergence of Inositol Polyphosphate 5-Phosphatases in Angiosperms
Abstract
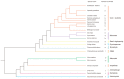
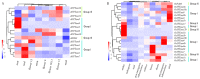
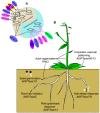
Inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase (5PTase), a key enzyme that hydrolyzes the 5` position of the inositol ring, has essential functions in growth, development, and stress responses in plants, yeasts, and animals. However, the evolutionary history and patterns of 5PTases have not been examined systematically. Here, we report a comprehensive molecular evolutionary analysis of the 5PTase gene family and define four groups. These four groups are different from former classifications, which were based on in vitro substrate specificity. Most orthologous groups appear to be conserved as single or low-copy genes in all lineages in Groups II-IV, whereas 5PTase genes in Group I underwent several duplication events in angiosperm, resulting in multiple gene copies. Whole-genome duplication (WGD) was the main mechanism for 5PTase duplications in angiosperm. Plant 5PTases have more members than that of animals, and most plant 5PTase genes appear to have evolved under strong purifying selection. The paralogs have diverged in substrate specificity and expression pattern, showing evidence of selection pressure. Meanwhile, the increase in 5PTases and divergences in sequence, expression, and substrate might have contributed to the divergent functions of 5PTase genes, allowing the angiosperms to successfully adapt to a great number of ecological niches.
Keywords: gene duplication; gene fate; inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase; phosphatidylinositol signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Expansion and Functional Divergence of Jumonji C-Containing Histone Demethylases: Significance of Duplications in Ancestral Angiosperms and Vertebrates.Plant Physiol. 2015 Aug;168(4):1321-37. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00520. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26059336 Free PMC article.
-
FRAGILE FIBER3, an Arabidopsis gene encoding a type II inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase, is required for secondary wall synthesis and actin organization in fiber cells.Plant Cell. 2004 Dec;16(12):3242-59. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.027466. Epub 2004 Nov 11. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 15539468 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and biochemical characterization of three WD-repeat-domain-containing inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatases in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell Physiol. 2004 Nov;45(11):1720-8. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pch187. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15574849
-
The Function of Inositol Phosphatases in Plant Tolerance to Abiotic Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 16;20(16):3999. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163999. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31426386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatases in cellular function and human disease.Biochem J. 2009 Apr 1;419(1):29-49. doi: 10.1042/BJ20081673. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19272022 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Male Sterile Anthers Induced by High Temperature in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Front Plant Sci. 2021 Oct 25;12:727966. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.727966. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34759937 Free PMC article.
-
KRN5b regulates maize kernel row number through mediating phosphoinositol signalling.Plant Biotechnol J. 2024 Dec;22(12):3427-3441. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14463. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Plant Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 39302972 Free PMC article.
-
Signalling Pinpointed to the Tip: The Complex Regulatory Network That Allows Pollen Tube Growth.Plants (Basel). 2020 Aug 26;9(9):1098. doi: 10.3390/plants9091098. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32859043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ectopic Expression of Gs5PTase8, a Soybean Inositol Polyphosphate 5-Phosphatase, Enhances Salt Tolerance in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 4;21(3):1023. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031023. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32033113 Free PMC article.
-
A putative tomato inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase, Le5PT1, is involved in plant growth and abiotic stress responses.3 Biotech. 2020 Jan;10(1):28. doi: 10.1007/s13205-019-2023-y. Epub 2020 Jan 4. 3 Biotech. 2020. PMID: 31950007 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

