Edwardsiella piscicida: A versatile emerging pathogen of fish
- PMID: 31122125
- PMCID: PMC6592360
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2019.1621648
Edwardsiella piscicida: A versatile emerging pathogen of fish
Abstract
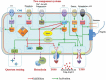
Edwardsiella piscicida is an Enterobacteriaceae that is abundant in water and causes food and waterborne infections in fish, animals, and humans. The bacterium causes Edwardsiellosis in farmed fish and can lead to severe economic losses in aquaculture worldwide. E. piscicida is an intracellular pathogen that can also cause systemic infection. Type III and type VI secretion systems are the bacterium's most lethal weapons against host defenses. It also possesses multi-antibiotic resistant genes and is selected and enriched in the environment due to the overuse of antibiotics. Therefore, the bacterium has great potential to contribute to the evolution of the resistome. All these properties have made this bacterium a perfect model to study bacteria virulence mechanisms and the spread of antimicrobial genes in the environment. We summarize recent advance in E. piscicida biology and provide insights into future research in virulence mechanisms, vaccine development and novel therapeutics.
Keywords: T3SS/T6SS and effectors; intracellular and systemic infection; resistome; virulence mechanisms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Balanced role of T3SS and T6SS in contribution to the full virulence of Edwardsiella piscicida.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Oct;93:871-878. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.08.014. Epub 2019 Aug 7. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31400510
-
Transcriptomic dissection of the horizontally acquired response regulator EsrB reveals its global regulatory roles in the physiological adaptation and activation of T3SS and the cognate effector repertoire in Edwardsiella piscicida during infection toward turbot.Virulence. 2017 Oct 3;8(7):1355-1377. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2017.1323157. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Virulence. 2017. PMID: 28441105 Free PMC article.
-
YebC controls virulence by activating T3SS gene expression in the pathogen Edwardsiella piscicida.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2018 Jul 1;365(14). doi: 10.1093/femsle/fny137. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29901702
-
Edwardsiella piscicida: a significant bacterial pathogen of cultured fish.Dis Aquat Organ. 2018 Oct 16;131(1):59-71. doi: 10.3354/dao03281. Dis Aquat Organ. 2018. PMID: 30324915 Review.
-
Antitoxin HigA orchestrates T3SS/T6SS expression in aquatic pathogen Edwardsiella piscicida.Microbiol Res. 2025 Nov;300:128281. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2025.128281. Epub 2025 Jul 17. Microbiol Res. 2025. PMID: 40684687 Review.
Cited by
-
The Changing Face of the Family Enterobacteriaceae (Order: "Enterobacterales"): New Members, Taxonomic Issues, Geographic Expansion, and New Diseases and Disease Syndromes.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021 Feb 24;34(2):e00174-20. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00174-20. Print 2021 Mar 17. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33627443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenicity and virulence of Aeromonas schubertii in farmed Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) in Thailand.BMC Vet Res. 2025 Jul 26;21(1):493. doi: 10.1186/s12917-025-04940-4. BMC Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40713821 Free PMC article.
-
Baicalin enhances antioxidant, inflammatory defense, and microbial diversity of yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) infected with Aeromonas hydrophila.Front Microbiol. 2024 Sep 20;15:1465346. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1465346. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39372274 Free PMC article.
-
The Involvement of Thiamine Uptake in the Virulence of Edwardsiella piscicida.Pathogens. 2022 Apr 13;11(4):464. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11040464. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35456139 Free PMC article.
-
Xenogeneic nucleoid-associated EnrR thwarts H-NS silencing of bacterial virulence with unique DNA binding.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Apr 22;50(7):3777-3798. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac180. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35325196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buján N, Toranzo AE, Magariños B. Edwardsiella piscicida: A significant bacterial pathogen of cultured fish. Dis Aquat Organ. 2018;131(1):59–71. - PubMed
-
- Grimont PA, Grimont F, Richard C, et al. Edwardsiella hoshinae, a new species of Enterobacteriaceae. Curr Microbiol. 1980;4(6):347–351.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
