Eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein as an oncogene in breast cancer
- PMID: 31122207
- PMCID: PMC6533768
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-5667-4
Eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein as an oncogene in breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 4E-Binding Protein (EIF4EBP1, 4EBP1) is overexpressed in many human cancers including breast cancer, yet the role of 4EBP1 in breast cancer remains understudied. Despite the known role of 4EBP1 as a negative regulator of cap-dependent protein translation, 4EBP1 is predicted to be an essential driving oncogene in many cancer cell lines in vitro, and can act as a driver of cancer cell proliferation. EIF4EBP1 is located within the 8p11-p12 genomic locus, which is frequently amplified in breast cancer and is known to predict poor prognosis and resistance to endocrine therapy.
Methods: Here we evaluated the effect of 4EBP1 targeting using shRNA knock-down of expression of 4EBP1, as well as response to the mTORC targeted drug everolimus in cell lines representing different breast cancer subtypes, including breast cancer cells with the 8p11-p12 amplicon, to better define a context and mechanism for oncogenic 4EBP1.
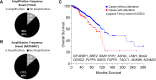
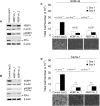
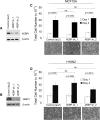
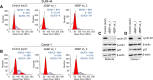
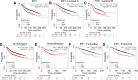
Results: Using a genome-scale shRNA screen on the SUM panel of breast cancer cell lines, we found 4EBP1 to be a strong hit in the 8p11 amplified SUM-44 cells, which have amplification and overexpression of 4EBP1. We then found that knock-down of 4EBP1 resulted in dramatic reductions in cell proliferation in 8p11 amplified breast cancer cells as well as in other luminal breast cancer cell lines, but had little or no effect on the proliferation of immortalized but non-tumorigenic human mammary epithelial cells. Kaplan-Meier analysis of EIF4EBP1 expression in breast cancer patients demonstrated that overexpression of this gene was associated with reduced relapse free patient survival across all breast tumor subtypes.
Conclusions: These results are consistent with an oncogenic role of 4EBP1 in luminal breast cancer and suggests a role for this protein in cell proliferation distinct from its more well-known role as a regulator of cap-dependent translation.
Keywords: 4E-BP1; 4EBP1; 8p11-p12; 8p11–12; 8p12–11; Amplification; Breast cancer; Chromosomal abnormality; Driver; EIF4EBP1; Estrogen receptor; Oncogene; PHAS-I.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
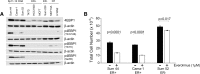

Similar articles
-
High-resolution genomic analysis of the 11q13 amplicon in breast cancers identifies synergy with 8p12 amplification, involving the mTOR targets S6K2 and 4EBP1.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2011 Oct;50(10):775-87. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20900. Epub 2011 Jul 11. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21748818
-
The mTOR effectors 4EBP1 and S6K2 are frequently coexpressed, and associated with a poor prognosis and endocrine resistance in breast cancer: a retrospective study including patients from the randomised Stockholm tamoxifen trials.Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(5):R96. doi: 10.1186/bcr3557. Breast Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24131622 Free PMC article.
-
KAT6A, a chromatin modifier from the 8p11-p12 amplicon is a candidate oncogene in luminal breast cancer.Neoplasia. 2014 Aug;16(8):644-55. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2014.07.007. Neoplasia. 2014. PMID: 25220592 Free PMC article.
-
Amplification of 8p11.23 in cancers and the role of amplicon genes.Life Sci. 2021 Jan 1;264:118729. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118729. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33166592 Review.
-
4E-BP1, a multifactor regulated multifunctional protein.Cell Cycle. 2016;15(6):781-6. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1151581. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 26901143 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The EIF4EBP1 gene encoding 4EBP1 is transcriptionally upregulated by MYC and linked to shorter survival in medulloblastoma.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Jul 16;11(1):330. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02601-x. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40670359 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1 (EIF4EBP1) expression in glioblastoma is driven by ETS1- and MYBL2-dependent transcriptional activation.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Feb 28;8(1):91. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00883-z. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 35228525 Free PMC article.
-
C8ORF88: A Novel eIF4E-Binding Protein.Genes (Basel). 2023 Nov 14;14(11):2076. doi: 10.3390/genes14112076. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38003019 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the oral administration of glycosaminoglycans with or without native type II collagen on the articular cartilage transcriptome in an osteoarthritic-induced rabbit model.Genes Nutr. 2024 Sep 4;19(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12263-024-00749-2. Genes Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39232650 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR pathway gene expression in association with race and clinicopathological characteristics in Black and White breast cancer patients.Discov Oncol. 2022 May 24;13(1):34. doi: 10.1007/s12672-022-00497-y. Discov Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35608730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Courjal F, et al. Mapping of DNA amplifications at 15 chromosomal localizations in 1875 breast tumors: definition of phenotypic groups. Cancer Res. 1997;57:4360–4367. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

