Surveillance of Unruptured Intracranial Saccular Aneurysms Using Noncontrast 3D-Black-Blood MRI: Comparison of 3D-TOF and Contrast-Enhanced MRA with 3D-DSA
- PMID: 31122914
- PMCID: PMC6582946
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A6080
Surveillance of Unruptured Intracranial Saccular Aneurysms Using Noncontrast 3D-Black-Blood MRI: Comparison of 3D-TOF and Contrast-Enhanced MRA with 3D-DSA
Erratum in
-
Erratum.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019 Oct;40(10):E63. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6206. Epub 2019 Sep 5. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019. PMID: 31488501 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
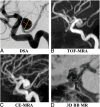
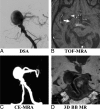
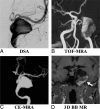
Background and purpose: Patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms routinely undergo surveillance imaging to monitor growth. Angiography is the criterion standard for aneurysm diagnosis, but it is invasive. This study aimed to evaluate the accuracy and reproducibility of a 3D noncontrast black-blood MR imaging technique for unruptured intracranial aneurysm measurement in comparison with 3D-TOF and contrast-enhanced MRA, using 3D rotational angiography as a reference standard.
Materials and methods: Sixty-four patients (57.3 ± 10.9 years of age, 41 women) with 68 saccular unruptured intracranial aneurysms were recruited. Patients underwent 3T MR imaging with 3D-TOF-MRA, 3D black-blood MR imaging, and contrast-enhanced MRA, and they underwent 3D rotational angiography within 2 weeks. The neck, width, and height of the unruptured intracranial aneurysms were measured by 2 radiologists independently on 3D rotational angiography and 3 MR imaging sequences. The accuracy and reproducibility were evaluated by Bland-Altman plots, the coefficient of variance, and the intraclass correlation coefficient.
Results: 3D black-blood MR imaging demonstrates the best agreement with DSA, with the smallest limits of agreement and measurement error (coefficients of variance range, 5.87%-7.04%). 3D-TOF-MRA had the largest limits of agreement and measurement error (coefficients of variance range, 12.73%-15.78%). The average coefficient of variance was 6.26% for 3D black-blood MR imaging, 7.03% for contrast-enhanced MRA, and 15.54% for TOF-MRA. No bias was found among 3 MR imaging sequences compared with 3D rotational angiography. All 3 MR imaging sequences had excellent interreader agreement (intraclass correlation coefficient, >0.95). 3D black-blood MR imaging performed the best for patients with intraluminal thrombus (n = 10).
Conclusions: 3D black-blood MR imaging achieves better accuracy for aneurysm size measurements compared with 3D-TOF, using 3D rotational angiography as a criterion standard. This noncontrast technique is promising for surveillance of unruptured intracranial aneurysms.
© 2019 by American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Figures

References
-
- Wiebers DO, Whisnant JP, Huston J 3rd, et al. ; International Study of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms Investigators. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet 2003;362:103–10 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13860-3 - DOI - PubMed
