Transcription-mediated replication hindrance: a major driver of genome instability
- PMID: 31123061
- PMCID: PMC6672053
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.324517.119
Transcription-mediated replication hindrance: a major driver of genome instability
Abstract
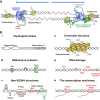
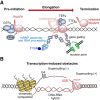
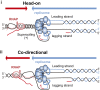
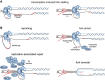
Genome replication involves dealing with obstacles that can result from DNA damage but also from chromatin alterations, topological stress, tightly bound proteins or non-B DNA structures such as R loops. Experimental evidence reveals that an engaged transcription machinery at the DNA can either enhance such obstacles or be an obstacle itself. Thus, transcription can become a potentially hazardous process promoting localized replication fork hindrance and stress, which would ultimately cause genome instability, a hallmark of cancer cells. Understanding the causes behind transcription-replication conflicts as well as how the cell resolves them to sustain genome integrity is the aim of this review.
Keywords: DNA–RNA hybrids; chromosome fragility; genetic instability; replication fork stalling; transcription.
© 2019 Gómez-González and Aguilera; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures