Clinical value of cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light chain in semantic dementia
- PMID: 31123142
- PMCID: PMC6820157
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp-2018-319784
Clinical value of cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light chain in semantic dementia
Abstract
Background: Semantic dementia (SD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterised by progressive language problems falling within the clinicopathological spectrum of frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD). The development of disease-modifying agents may be facilitated by the relative clinical and pathological homogeneity of SD, but we need robust monitoring biomarkers to measure their efficacy. In different FTLD subtypes, neurofilament light chain (NfL) is a promising marker, therefore we investigated the utility of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) NfL in SD.
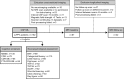
Methods: This large retrospective multicentre study compared cross-sectional CSF NfL levels of 162 patients with SD with 65 controls. CSF NfL levels of patients were correlated with clinical parameters (including survival), neuropsychological test scores and regional grey matter atrophy (including longitudinal data in a subset).
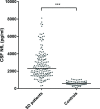
Results: CSF NfL levels were significantly higher in patients with SD (median: 2326 pg/mL, IQR: 1628-3593) than in controls (577 (446-766), p<0.001). Higher CSF NfL levels were moderately associated with naming impairment as measured by the Boston Naming Test (rs =-0.32, p=0.002) and with smaller grey matter volume of the parahippocampal gyri (rs =-0.31, p=0.004). However, cross-sectional CSF NfL levels were not associated with progression of grey matter atrophy and did not predict survival.
Conclusion: CSF NfL is a promising biomarker in the diagnostic process of SD, although it has limited cross-sectional monitoring or prognostic abilities.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors report no conflicts of interest relevant to this study. LHHM is supported by Alzheimer Nederland (grant number WE.09 2014 04). ALB and JCR are supported by the NIH (U54NS092089, R01AG031278, R01AG038791, R01AG032306, R01AG022983) and the Association for Frontotemporal Degeneration. ALB, JCR and LDK are supported by the Bluefield Project to Cure Frontotemporal Dementia. The Dementia Research Centre is supported by Alzheimer’s Research UK, Brain Research Trust and The Wolfson Foundation. This work was supported by the NIHR Queen Square Dementia Biomedical Research Unit, the NIHR UCL/H Biomedical Research Centre and the Leonard Wolfson Experimental Neurology Centre (LWENC) Clinical Research Facility as well as an Alzheimer’s Society grant (AS-PG-16-007). JDR is supported by an MRC Clinician Scientist Fellowship (MR/M008525/1) and has received funding from the NIHR Rare Disease Translational Research Collaboration (BRC149/NS/MH). IOCW is supported by an MRC Clinical Research Training Fellowship (MR/M018288/1). AS is supported by the Swedish Society for Medical Research. CET is supported by ZonMW Memorabel Program (grant number 733050206). JCvS is supported by the Dioraphte Foundation.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 AG032953/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG038791/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052943/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG023481/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG019724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032306/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG066597/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/J009482/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K23 AG059888/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M023664/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 NS109260/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AG043503/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M018288/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M008525/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K23 NS088341/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AG045333/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG031278/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG017586/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG038490/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG022983/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS092089/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
