Complications of Percutaneous Renal Biopsy
- PMID: 31123379
- PMCID: PMC6531025
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0039-1688422
Complications of Percutaneous Renal Biopsy
Abstract
Percutaneous renal biopsy is widely used for diagnosis, prognosis, and management of nephropathies. Complications may arise after renal biopsy, most commonly in the form of bleeding. Efforts should be taken to optimize modifiable risk factors such as hypertension, thrombocytopenia, and coagulopathy prior to the procedure. Unmodifiable risk factors such as poor renal function, gender, and underlying histologic diagnosis may be used to identify high-risk patients. Delayed presentation of bleeding complications is common, and close clinical follow-up is crucial.
Keywords: bleeding complication; embolization; hemorrhage; interventional radiology; renal biopsy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
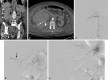
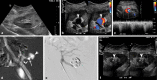
References
-
- Iversen P, Brun C. Aspiration biopsy of the kidney. Am J Med. 1951;11(03):324–330. - PubMed
-
- Kark R M, Muehrcke R C.Biopsy of kidney in prone position Lancet 1954266(6821):1047–1049. - PubMed
-
- Madaio M P. Renal biopsy. Kidney Int. 1990;38(03):529–543. - PubMed
-
- Korbet S M. Percutaneous renal biopsy. Semin Nephrol. 2002;22(03):254–267. - PubMed

