Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors as novel agents in improving survival in diabetic patients with colorectal cancer and lung cancer: A Surveillance Epidemiology and Endpoint Research Medicare study
- PMID: 31124302
- PMCID: PMC6639187
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2278
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors as novel agents in improving survival in diabetic patients with colorectal cancer and lung cancer: A Surveillance Epidemiology and Endpoint Research Medicare study
Abstract
Background: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) is a cell surface protein that can act as a tumor suppressor or activator, depending upon the level of expression and interaction with the microenvironment and chemokines. DPP4 inhibitors are used to treat diabetes.
Methods: We conducted this Surveillance Epidemiology and Endpoint Research-Medicare database study to evaluate the role of DPP4 inhibitors on the overall survival (OS) of diabetic patients diagnosed with colorectal (CRC) and lung cancers.
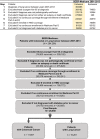
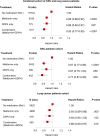
Results: Diabetic patients with CRC or lung cancer who were treated with DPP4 inhibitors exhibited a statistically significant survival advantage (hazard ratio [HR] of 0.89; CI: 0.82-0.97, P = 0.007) that remained significant after controlling for all other confounders. When DPP4 inhibitors were used in combination of metformin which is known to suppress cancer, the survival advantage was even more pronounced (HR of 0.83; CI: 0.77-0.90, P < 0.0001). Data were then analyzed separately for two cancer types. In the CRC-only cohort, the use of DPP4 inhibitors alone had a positive trend but did not meet statistically significant threshold (HR of 0.87; CI: 0.75-1.00, P = 0.055), while the combined use of DPP4 inhibitors and metformin was associated with statistically significant survival advantage (HR of 0.77; CI: 0.67-0.89, P = 0.003). Similarly, for the lung cancer cohort, use of DPP4 alone was not found to be statistically significant (HR of 0.93; CI: 0.83-1.03, P = 0.153), whereas lung cancer patients treated with the combination of DPP4 inhibitors and metformin showed statistically significant survival advantage (HR of 0.88; CI: 0.80-0.97, P = 0.010).
Conclusions: DPP4 inhibition in CRC and lung cancer is associated with improved OS, which possibly may be due to the effect of DPP4 inhibition on immunoregulation of cancer.
Keywords: CD26; DPP4 inhibitors; SEER-Medicare; colorectal cancer; lung cancer.
© 2019 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparative Safety of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors Versus Sulfonylureas and Other Glucose-lowering Therapies for Three Acute Outcomes.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 11;8(1):15142. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33483-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30310100 Free PMC article.
-
Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors vs Metformin for New-onset Dementia: A Propensity Score-matched Cohort Study.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025 Feb 18;110(3):e650-e659. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgae281. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025. PMID: 38652239
-
Role of pre-existing type 2 diabetes in colorectal cancer survival among older Americans: a SEER-Medicare population-based study 2002-2011.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2019 Aug;34(8):1467-1475. doi: 10.1007/s00384-019-03345-8. Epub 2019 Jul 9. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2019. PMID: 31289849
-
Prognostic role of metformin intake in diabetic patients with colorectal cancer: An updated qualitative evidence of cohort studies.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 18;8(16):26448-26459. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14688. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28103573 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting cluster of differentiation 26 / dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (CD26/DPP4) in organ fibrosis.Br J Pharmacol. 2023 Nov;180(22):2846-2861. doi: 10.1111/bph.15967. Epub 2022 Nov 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36196001 Review.
Cited by
-
CD26/DPP-4: Type 2 Diabetes Drug Target with Potential Influence on Cancer Biology.Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 2;13(9):2191. doi: 10.3390/cancers13092191. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34063285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) reduce the diffusion of doxorubicin which may attenuate its ability to induce apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells.Heliyon. 2022 Jun 15;8(6):e09730. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09730. eCollection 2022 Jun. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35756123 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors May Change the Development of Urinary Tract and Hematological Malignancies as Compared With Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors: Data of the Post-Hoc Analysis of a Nationwide Study.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 28;11:725465. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.725465. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34778040 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Insulin Antidiabetic Agents and Lung Cancer Risk in Drug-Naive Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 28;16(13):2377. doi: 10.3390/cancers16132377. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001440 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin Remodeling of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis is Mediated by an HGF-PU.1-DPP4 Axis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Oct;8(19):e2004673. doi: 10.1002/advs.202004673. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34378358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Havre P, Abe M, Urasaki Y, Ohnuma K, Morimoto C, Dang N. The role of CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV in cancer. Front Biosci. 2008;13:1634‐1645. - PubMed
-
- Pro B, Dang N. CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV and its role in cancer. Histol Histopathol. 2004;19(4):1345‐1351. - PubMed
-
- Beckenkamp A, Davies S, Willig J, Buffon A. DPPIV/CD26: a tumor suppressor or a marker of malignancy? Tumor Biol. 2016;37(6):7059‐7073. - PubMed
-
- Lee J‐J, Wang T‐Y, Liu C‐L, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV as a prognostic marker and therapeutic target in papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(8):2930‐2940. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

