Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors as novel agents in improving survival in diabetic patients with colorectal cancer and lung cancer: A Surveillance Epidemiology and Endpoint Research Medicare study
- PMID: 31124302
- PMCID: PMC6639187
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2278
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors as novel agents in improving survival in diabetic patients with colorectal cancer and lung cancer: A Surveillance Epidemiology and Endpoint Research Medicare study
Abstract
Background: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) is a cell surface protein that can act as a tumor suppressor or activator, depending upon the level of expression and interaction with the microenvironment and chemokines. DPP4 inhibitors are used to treat diabetes.
Methods: We conducted this Surveillance Epidemiology and Endpoint Research-Medicare database study to evaluate the role of DPP4 inhibitors on the overall survival (OS) of diabetic patients diagnosed with colorectal (CRC) and lung cancers.
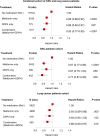
Results: Diabetic patients with CRC or lung cancer who were treated with DPP4 inhibitors exhibited a statistically significant survival advantage (hazard ratio [HR] of 0.89; CI: 0.82-0.97, P = 0.007) that remained significant after controlling for all other confounders. When DPP4 inhibitors were used in combination of metformin which is known to suppress cancer, the survival advantage was even more pronounced (HR of 0.83; CI: 0.77-0.90, P < 0.0001). Data were then analyzed separately for two cancer types. In the CRC-only cohort, the use of DPP4 inhibitors alone had a positive trend but did not meet statistically significant threshold (HR of 0.87; CI: 0.75-1.00, P = 0.055), while the combined use of DPP4 inhibitors and metformin was associated with statistically significant survival advantage (HR of 0.77; CI: 0.67-0.89, P = 0.003). Similarly, for the lung cancer cohort, use of DPP4 alone was not found to be statistically significant (HR of 0.93; CI: 0.83-1.03, P = 0.153), whereas lung cancer patients treated with the combination of DPP4 inhibitors and metformin showed statistically significant survival advantage (HR of 0.88; CI: 0.80-0.97, P = 0.010).
Conclusions: DPP4 inhibition in CRC and lung cancer is associated with improved OS, which possibly may be due to the effect of DPP4 inhibition on immunoregulation of cancer.
Keywords: CD26; DPP4 inhibitors; SEER-Medicare; colorectal cancer; lung cancer.
© 2019 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Havre P, Abe M, Urasaki Y, Ohnuma K, Morimoto C, Dang N. The role of CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV in cancer. Front Biosci. 2008;13:1634‐1645. - PubMed
-
- Pro B, Dang N. CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV and its role in cancer. Histol Histopathol. 2004;19(4):1345‐1351. - PubMed
-
- Beckenkamp A, Davies S, Willig J, Buffon A. DPPIV/CD26: a tumor suppressor or a marker of malignancy? Tumor Biol. 2016;37(6):7059‐7073. - PubMed
-
- Lee J‐J, Wang T‐Y, Liu C‐L, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV as a prognostic marker and therapeutic target in papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(8):2930‐2940. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

