Effect of Cardiac Rehabilitation on Outcomes in Patients with ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 31124336
- PMCID: PMC6536392
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.6.535
Effect of Cardiac Rehabilitation on Outcomes in Patients with ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
Purpose: Whether cardiac rehabilitation (CR) improves clinical outcomes in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with drug-eluting stents (DESs) has not been thoroughly evaluated. Moreover, few studies have sought to identify patients who would benefit most from CR among STEMI patients.
Materials and methods: Consecutively, 265 STEMI patients who underwent primary PCI with implantation of DESs and follow-up angiography were examined. Seventy-six patients (30%) who received CR were assigned to the CR+ group. Another 178 patients (70%) who did not participate in CR were assigned to the CR- group. Second generation DESs were implanted in 238 (94%) patients.
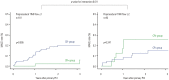
Results: Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), including death, myocardial infarction, and revascularization, were compared. The CR+ group tended to have lower MACE than the CR- group at 3 years, although the difference was not statistically significant (9.9% vs. 18.3%, hazard ratio=0.54, p=0.138). Subgroup analysis revealed a significant interaction according to CR and preprocedural thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) flow (p value for interaction=0.011). In patients with low preprocedural TIMI flow (TIMI flow ≤1, n=161), those in the CR+ group had significantly lower MACE than those in the CR- group (p=0.005), whereas MACE was not different among patients with higher TIMI flow (TIMI flow ≥2, n=93).
Conclusion: CR including exercise training was associated with lower MACE, particularly in patients with lower preprocedural TIMI flow during primary PCI for STEMI in the current DES era.
Keywords: Cardiac rehabilitation; drug eluting stent; myocardial infarction.
© Copyright: Yonsei University College of Medicine 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Twelve-month clinical outcomes of acute non-ST versus ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients with reduced preprocedural thrombolysis in myocardial infarction flow undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention.Coron Artery Dis. 2018 Aug;29(5):416-422. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0000000000000632. Coron Artery Dis. 2018. PMID: 29708887
-
[Impact of inflammatory reaction levels and culprit plaque characteristics on preprocedural thrombolysis in myocardial infarction flow grade in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2021 Feb 24;49(2):150-157. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20200531-00452. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33611901 Chinese.
-
Prediabetes versus type 2 diabetes mellitus based on pre-percutaneous coronary intervention thrombolysis in myocardial infarction flow grade in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction after successful newer-generation drug-eluting stent implantation.Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2021 Jan-Feb;18(1):1479164121991505. doi: 10.1177/1479164121991505. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2021. PMID: 33535819 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical outcomes of complete revascularization using either angiography-guided or fractional flow reserve-guided drug-eluting stent implantation in non-culprit vessels in ST elevation myocardial infarction patients: insights from a study based on a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018 Sep;34(9):1349-1364. doi: 10.1007/s10554-018-1362-9. Epub 2018 May 19. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29779179
-
Intravascular Ultrasound-Guided versus Angiography-Guided Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for Stent Thrombosis Elevation Myocardial Infarction: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cardiology. 2024;149(3):196-204. doi: 10.1159/000537682. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Cardiology. 2024. PMID: 38350431
Cited by
-
Adherence to Cardiac Rehabilitation in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction After PCI: A Scoping Review.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 Aug 28;17:4165-4176. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S483512. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 39220330 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Buqi Huoxue Decoction Combined with Cardiac Rehabilitation Nursing after Coronary Intervention in Patients with Acute ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction and Its Influence on Prognosis.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Mar 19;2022:4008966. doi: 10.1155/2022/4008966. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. Retraction in: J Healthc Eng. 2023 Oct 4;2023:9787942. doi: 10.1155/2023/9787942. PMID: 35345661 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
Exercise Training and Cardiac Rehabilitation in Patients After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Comprehensive Assessment and Prescription.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 27;14(5):1607. doi: 10.3390/jcm14051607. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40095584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Beneficial Role of Exercise Training for Myocardial Infarction Treatment in Elderly.Front Physiol. 2020 Apr 24;11:270. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00270. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32390856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac Rehabilitation of Patients with Acute ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Undergoing Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in a Han Population in Northern China: A Prospective Cohort Study.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Aug 28;14:4959-4965. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S326725. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34483684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taylor RS, Brown A, Ebrahim S, Jolliffe J, Noorani H, Rees K, et al. Exercise-based rehabilitation for patients with coronary heart disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Med. 2004;116:682–692. - PubMed
-
- Clark AM, Hartling L, Vandermeer B, McAlister FA. Meta-analysis: secondary prevention programs for patients with coronary artery disease. Ann Intern Med. 2005;143:659–672. - PubMed
-
- Hambrecht R, Walther C, Möbius-Winkler S, Gielen S, Linke A, Conradi K, et al. Percutaneous coronary angioplasty compared with exercise training in patients with stable coronary artery disease: a randomized trial. Circulation. 2004;109:1371–1378. - PubMed
-
- Pouche M, Ruidavets JB, Ferrières J, Iliou MC, Douard H, Lorgis L, et al. Cardiac rehabilitation and 5-year mortality after acute coronary syndromes: The 2005 French FAST-MI study. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2016;109:178–187. - PubMed
-
- Cottin Y, Cambou JP, Casillas JM, Ferrières J, Cantet C, Danchin N. Specific profile and referral bias of rehabilitated patients after an acute coronary syndrome. J Cardiopulm Rehabil. 2004;24:38–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

