Effect of intravitreal and intraperitoneal cyanidin-3-glucoside injection in oxygen-induced retinopathy mouse model
- PMID: 31124490
- PMCID: PMC6552572
- DOI: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_166_18
Effect of intravitreal and intraperitoneal cyanidin-3-glucoside injection in oxygen-induced retinopathy mouse model
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the effect of cyanidin-3-glucoside (C3G) in oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR) mouse model.
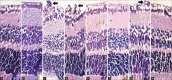
Methods: In this experimental study, 10 C57BL / 6J type mice exposed to room air comprised two control groups (n = 5 each; a negative control and a group receiving intravitreal sterile dimethyl sulfoxide [IVS DMSO]). Thirty C57BL / 6J type mice exposed to 75% ± 2% oxygen from postnatal day 7 to postnatal day 12 comprised the OIR groups. On postnatal day 12, these mice were randomized into six groups (n = 5 each): two OIR control groups (negative control and IVS DMSO), two intravitreal C3G groups (300 and 600 ng/μL), and two intraperitoneal C3G groups (0.05 and 0.1 mg/kg). We quantified neovascularization by counting endothelial cell proliferation on the vitreal side of the inner limiting membrane of the retina and examined histological and ultrastructural changes via light and electron microscopy and apoptosis by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase deoxy-UTP-nick end labeling.
Results: The intravitreal C3G groups yielded lower endothelial cell counts compared with the intravitreal DMSO group. The intraperitoneal high-dose group had lower cell counts compared with the OIR control groups. Electron microscopy revealed significantly less mitochondrial dysmorphology in intravitreal groups and the high-dose intraperitoneal mice. We noted no difference in apoptotic cell count between the controls, low-dose intravitreal, and both intraperitoneal groups. However, apoptotic cell count was significantly higher in the high-dose intravitreal group.
Conclusion: C3G suppresses endothelial cell proliferation in an OIR mouse model, leads to a reduced hyperoxia-induced mitochondrial dysmorphology, but increases apoptotic cell death in high concentrations.
Keywords: Anthocyanin; cyanidin-3-glucoside; oxygen-induced retinopathy mouse model; retinal vascular disease; retinopathy of prematurity.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural consequences after intravitreal bevacizumab injection without increasing apoptotic cell death in a retinopathy of prematurity mouse model.Acta Ophthalmol. 2012 Sep;90(6):564-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.2010.01963.x. Epub 2010 Aug 4. Acta Ophthalmol. 2012. PMID: 20698831
-
Antiproliferative and Mitochondrial Protective Effects of Apigenin in an Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy In Vivo Mouse Model.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Dec;37(10):580-590. doi: 10.1089/jop.2021.0046. Epub 2021 Oct 15. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34665015
-
Antiproliferative and anti-apoptotic effect of astaxanthin in an oxygen-induced retinopathy mouse model.Can J Ophthalmol. 2019 Feb;54(1):65-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjo.2018.02.017. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Can J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 30851776
-
[The effect of semaphorin 3A in the process of apoptosis in oxygen induced retinopathy in rats].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Jun;50(6):440-7. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25241977 Chinese.
-
Retinal vascular injuries and intravitreal human embryonic stem cell-derived haemangioblasts.Acta Ophthalmol. 2017 Sep;95(6):e468-e476. doi: 10.1111/aos.13477. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28636206
Cited by
-
Inherited Retinal Dystrophies: Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Their Physiopathology and Therapeutic Implications.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 May 30;11(6):1086. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061086. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35739983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effect of Total Panax Notoginseng Saponins on Retinal Ganglion Cells of an Optic Nerve Crush Injury Rat Model.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Aug 4;2021:4356949. doi: 10.1155/2021/4356949. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34395614 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen toxicity: cellular mechanisms in normobaric hyperoxia.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023 Feb;39(1):111-143. doi: 10.1007/s10565-022-09773-7. Epub 2022 Sep 16. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36112262 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asano MK, Dray PB. Retinopathy of prematurity. Dis Mon. 2014;60:282–291. - PubMed
-
- Cavallaro G, Filippi L, Bagnoli P, La Marca G, Cristofori G, Raffaeli G, et al. The pathophysiology of retinopathy of prematurity: An update of previous and recent knowledge. Acta Ophthalmol. 2014;92:2–20. - PubMed
-
- Beauchamp MH, Marrache AM, Hou X, Gobeil F, Jr, Bernier SG, Lachapelle P, et al. Platelet-activating factor in vasoobliteration of oxygen-induced retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002;43:3327–37. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

