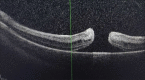
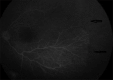
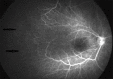
The safety and effectiveness of 0.16 mg bevacizumab plus or minus additional laser photocoagulation in the treatment of retinopathy of prematurity
- PMID: 31124508
- PMCID: PMC6552615
- DOI: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_2115_18
The safety and effectiveness of 0.16 mg bevacizumab plus or minus additional laser photocoagulation in the treatment of retinopathy of prematurity
Abstract
Purpose: Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) is the leading cause of preventable blindness in premature infants. Antivascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) therapy has been used increasingly in treatment as a pharmacological alternative to laser therapy. In this study, we evaluate the results of low-dose anti-VEGF treatments.
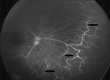
Methods: Design: Retrospective--observational study. Infants who had been evaluated for ROP disease between February 2016 and February 2017 were assessed. We retrospectively reviewed the ROP stages, treatment results, and complications. Laser photocoagulation (LPC) and intravitreal bevacizumab (0.16 mg IVB) were used for treatment and fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) was also performed in some of the cases.
Results: IVB was applied to 43 infants. A macular hole was seen in one infant's eye after IVB. LPC was applied to avascular areas in 21 infants. In three patients, persistence of the disease was observed after administration of a low dose of IVB. Additional LFK was performed in these patients. None of the infants who received LPC had any complications.
Conclusion: IVB is increasingly becoming the first-line treatment for ROP. For severe ROP, 0.16 mg IVB is effective. Using LPC to treat avascular areas after 70 weeks' gestational age (GA) may decrease the risk of late recurrence and appears to be a safe treatment to use.
Keywords: Complication; laser photocoagulation; macular hole; retinopathy of prematurity; ultra-low-dose bevacizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- Zin A, Gole GA. Retinopathy of prematurity-incidence today. Clin Perinatol. 2013;40:185–200. - PubMed
-
- Ergenekon E, Turan O, Ozdek S. Retinopathy of prematurity in Turkey. Cocuk Sagligi ve Hastalýklari Dergisi. 2010;53:4–9.
-
- Fierson WM. Screening examination of premature infants for retinopathy of prematurity. Pediatrics. 2013;133:189–95. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert G. Retinopathy of prematurity a global perspective of epidemics, population of babies at risk and implications for control. Early Hum Dev. 2008;84:77–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources