KLF8 is associated with poor prognosis and regulates glycolysis by targeting GLUT4 in gastric cancer
- PMID: 31124603
- PMCID: PMC6653475
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14378
KLF8 is associated with poor prognosis and regulates glycolysis by targeting GLUT4 in gastric cancer
Abstract
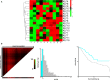
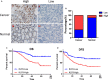
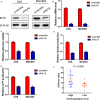
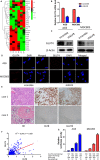
Krüppel-like transcription factor (KLF) family is involved in tumorigenesis in different types of cancer. However, the importance of KLF family in gastric cancer is unclear. Here, we examined KLF gene expression in five paired liver metastases and primary gastric cancer tissues by RT-PCR, and immunohistochemistry was used to study KLF8 expression in 206 gastric cancer samples. The impact of KLF8 expression on glycolysis, an altered energy metabolism that characterizes cancer cells, was evaluated. KLF8 showed the highest up-regulation in liver metastases compared with primary tumours among all KLF members. Higher KLF8 expression associated with larger tumour size (P < 0.001), advanced T stage (P = 0.003) and N stage (P < 0.001). High KLF8 expression implied shorter survival outcome in both TCGA and validation cohort (P < 0.05). Silencing KLF8 expression impaired the glycolysis rate of gastric cancer cells in vitro. Moreover, high KLF8 expression positively associated with SUVmax in patient samples. KLF8 activated the GLUT4 promoter activity in a dose-dependent manner (P < 0.05). Importantly, KLF8 and GLUT4 showed consistent expression patterns in gastric cancer tissues. These findings suggest that KLF8 modulates glycolysis by targeting GLUT4 and could serve as a novel biomarker for survival and potential therapeutic target in gastric cancer.
Keywords: KLF8; Warburg effect; gastric cancer; prognosis.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Krüppel-like factor 8 overexpression is correlated with angiogenesis and poor prognosis in gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jul 21;19(27):4309-15. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i27.4309. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23885141 Free PMC article.
-
Krüppel-Like Factor 8 Overexpression Correlates with Poor Prognosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Pathol Oncol Res. 2019 Jan;25(1):115-121. doi: 10.1007/s12253-017-0321-4. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Pathol Oncol Res. 2019. PMID: 28986741
-
Krüppel-like factor 8 involved in hypoxia promotes the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer via epithelial to mesenchymal transition.Oncol Rep. 2014 Dec;32(6):2397-404. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3495. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Oncol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25333643
-
The level of Krüppel-like factor 8 expression predicts prognosis and metastasis in various carcinomas.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 May;98(18):e15519. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015519. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31045845 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Krüppel-like factor 8 in cancer biology: Current research and its clinical relevance.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Jan;183:114351. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114351. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33253644 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone methyltransferase SETD1A interacts with HIF1α to enhance glycolysis and promote cancer progression in gastric cancer.Mol Oncol. 2020 Jun;14(6):1397-1409. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12689. Epub 2020 Apr 26. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32291851 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of Solute carrier family-2 members reveals SLC2A4 as an independent favorable prognostic biomarker for breast cancer.Channels (Austin). 2021 Dec;15(1):555-568. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2021.1973788. Channels (Austin). 2021. PMID: 34488531 Free PMC article.
-
Krüppel-like factors in tumors: Key regulators and therapeutic avenues.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 25;13:1080720. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1080720. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36761967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs: novel actors of Wnt signaling pathway in lung cancer progression.EXCLI J. 2023 Jul 12;22:645-669. doi: 10.17179/excli2023-6209. eCollection 2023. EXCLI J. 2023. PMID: 37636026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The log odds of negative lymph nodes/T stage: a new prognostic and predictive tool for resected gastric cancer patients.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021 Aug;147(8):2259-2269. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03654-y. Epub 2021 May 18. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34003367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet‐Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA: A Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA: A Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–132. - PubMed
-
- Spolverato G, Ejaz A, Kim Y, et al. Rates and patterns of recurrence after curative intent resection for gastric cancer: a United States multi‐institutional analysis. J Am Coll Surg. 2014;219:664–675. - PubMed
-
- Wu CW, Lo SS, Shen KH, et al. Incidence and factors associated with recurrence patterns after intended curative surgery for gastric cancer. World J Surg. 2003;27:153–158. - PubMed
-
- Huang KH, Chen JH, Wu CW, et al. Factors affecting recurrence in node‐negative advanced gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:1522–1526. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

