Clinical utility of beta-hydroxybutyrate measurement in the management of physiological ketosis at home in children under 5
- PMID: 31124998
- PMCID: PMC6776208
- DOI: 10.23750/abm.v90i2.8260
Clinical utility of beta-hydroxybutyrate measurement in the management of physiological ketosis at home in children under 5
Abstract
Aim: To verify the possible advantages of 3- β-hydroxybutyrate (3HB) measurement compared to urinary assay of ketones during an intercurrent disease managed at home.
Methods: Twelve Pediatricians were asked to enroll at least 4 patients aged 3 to 5 years, affected by an intercurrent illness and showing at least one of symptoms reliable to ketosis. Recruited patients were submitted to the simultaneous assay of 3HB in capillary blood and ketones in urine at 3 (T3) and 6 hours (T6) from the first measurement (T0). For urinary and blood ketone detection commercial tests were used.
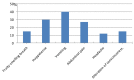
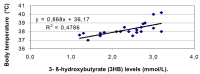
Results: Thirty-eight children (4.36±2.60 years old; 25 boys) were enrolled into the study. At T0 all children showed 3HB levels (1.2-3.2 mmol/L), but only 10 of them (26.3%) associated also urinary ketone bodies (2 to 4+). In response to 3 hour treatment (T3) with a glucose solution, 3HB values decreased in 19 (0,8-1,8 mmol/L) and normalized in 13 children (<0.2 mmol/L); while ketonuria disappeared in only 2 patients, it was confirmed in 8 and appeared (4+) the first time in the remaining 28 children. At T6 3HB levels fell definitively within the normal range in all children, while ketonuria was still present (2+) in 9 patients (23%). The pediatricians reported two limitations about blood 3HB dosage compared to the urinary test: the invasiveness of capillary blood collection, and the cost of supplies for finger pricking, reagent strips and reflectance meter.
Conclusions: 3HB monitor in capillary blood is more effective and clinically more useful in diagnosing and managing of an ongoing ketosis in children with a mild infective disease than ketones detection in the urine. These advantages are mitigated by the cost of 3HB measurement.
Conflict of interest statement
Each author declares that he or she has no commercial associations (e.g. consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangement etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article
Figures
References
-
- Koch DD, Feldbruegge DH. Optimized kinetic method for automated determination of beta-hydroxybutyrate. Clin Chem. 1987;33:1761–1766. - PubMed
-
- Byrne HA, Tuesnon KL, Hollis S, et al. Evaliation ofan Electromedical sensor for measuring blood ketone. Diabetes Care. 2000;23:500–5003. - PubMed
-
- Sena SF. Beta-hydroxybutyrate: New test for ketoacidosis. Tehinically speaking, Danbury Hospital, A high level of care. July 2010, vol 4, n 8
-
- Vanelli M, Chiari G, Capuano C, et al. T. The direct measurement of 3-B-hydroxybutyrate enhances the management of diabetic ketoacidosis in children and reduces time and costs of treatment. Diab Nutr Metab. 2003;16:312–316. - PubMed
-
- Brink S, Joel D, Laffel L, et al. Sick day management in children and adolescents with diabetes. Pediatric Diabetes. 2014;15(Suppl. 20):193–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical